Category: "Photos"
The cup and the butterfly
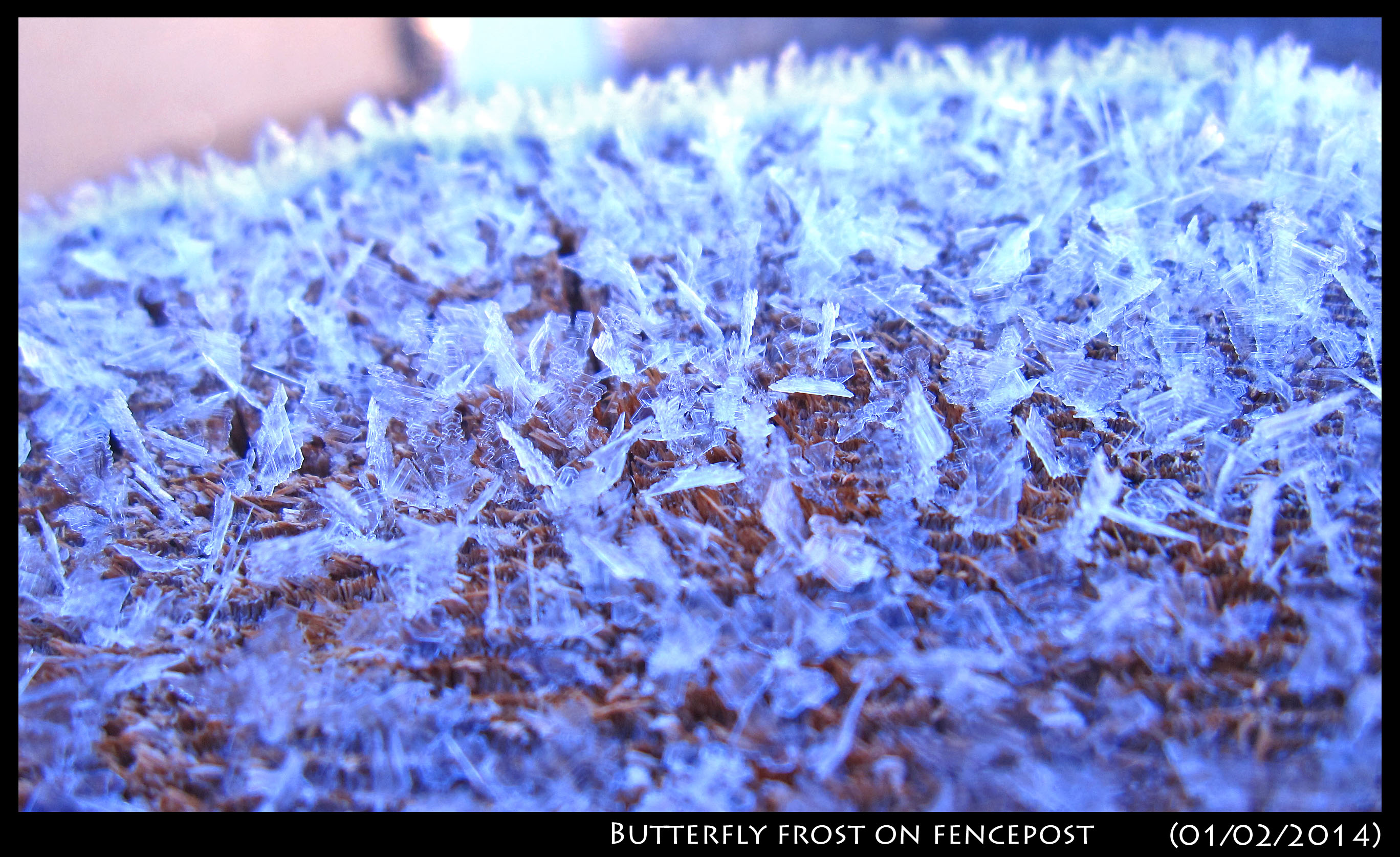
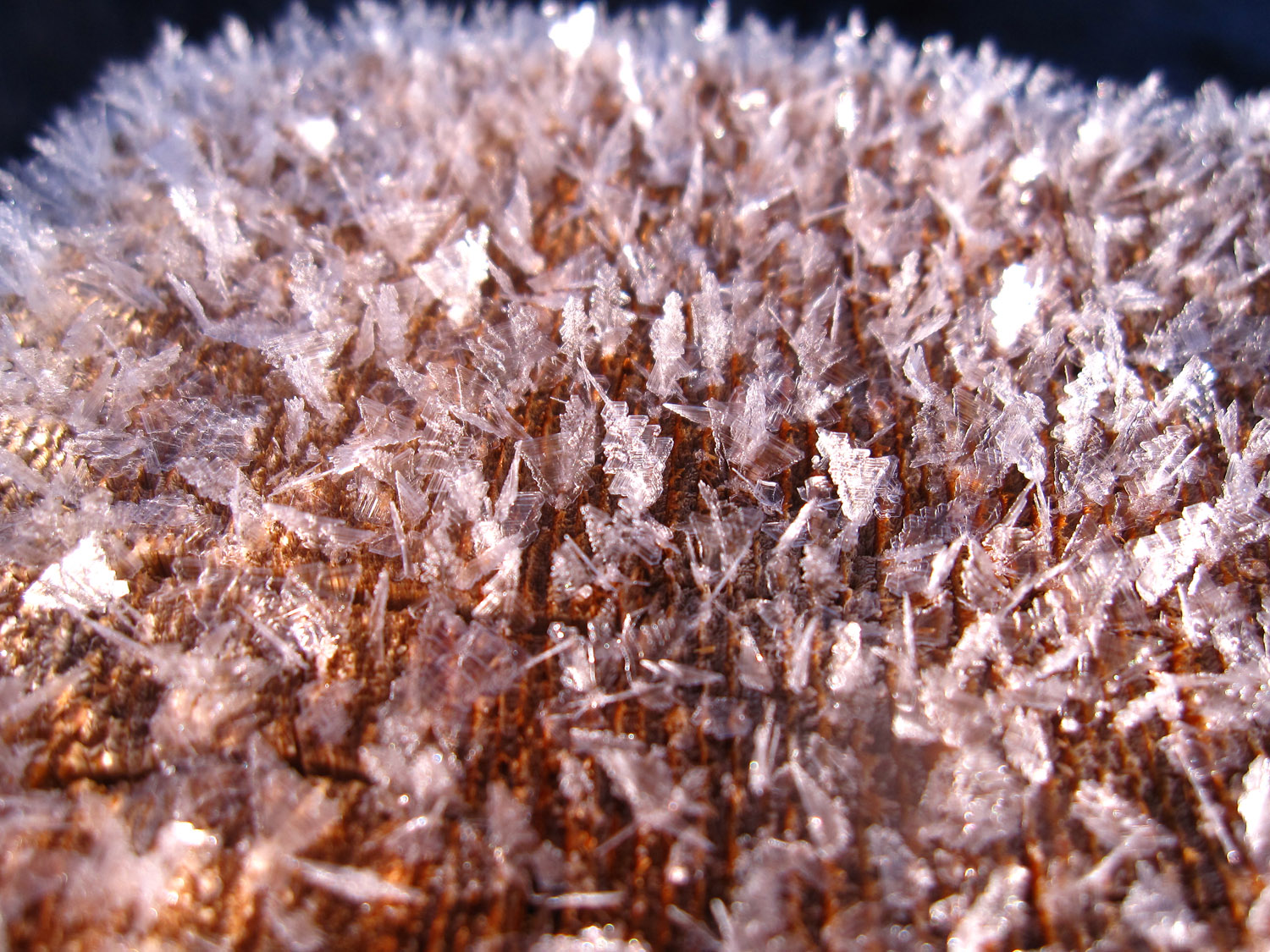
February 25th, 2014In early January, while visiting a cold, dry region, I saw this frost on a wooden fencepost.
The pattern resembled a cluster of butterflies. In the shade, these "butterflies" were blue, reflecting the blue sky. In the sun, they were bright white:
These are a type of hoar-frost, and though hoar-frost grows by the same processes as snow crystals, they can take on an even greater variety of forms. That they have more forms is a consequence of the fact that they can experience much greater levels of humidity, that is humidity relative to their temperature. This greater degree of humidity produces faster growth. Frost forms can also be more unusual because the proximity of the crystals alter the vapor gradients.
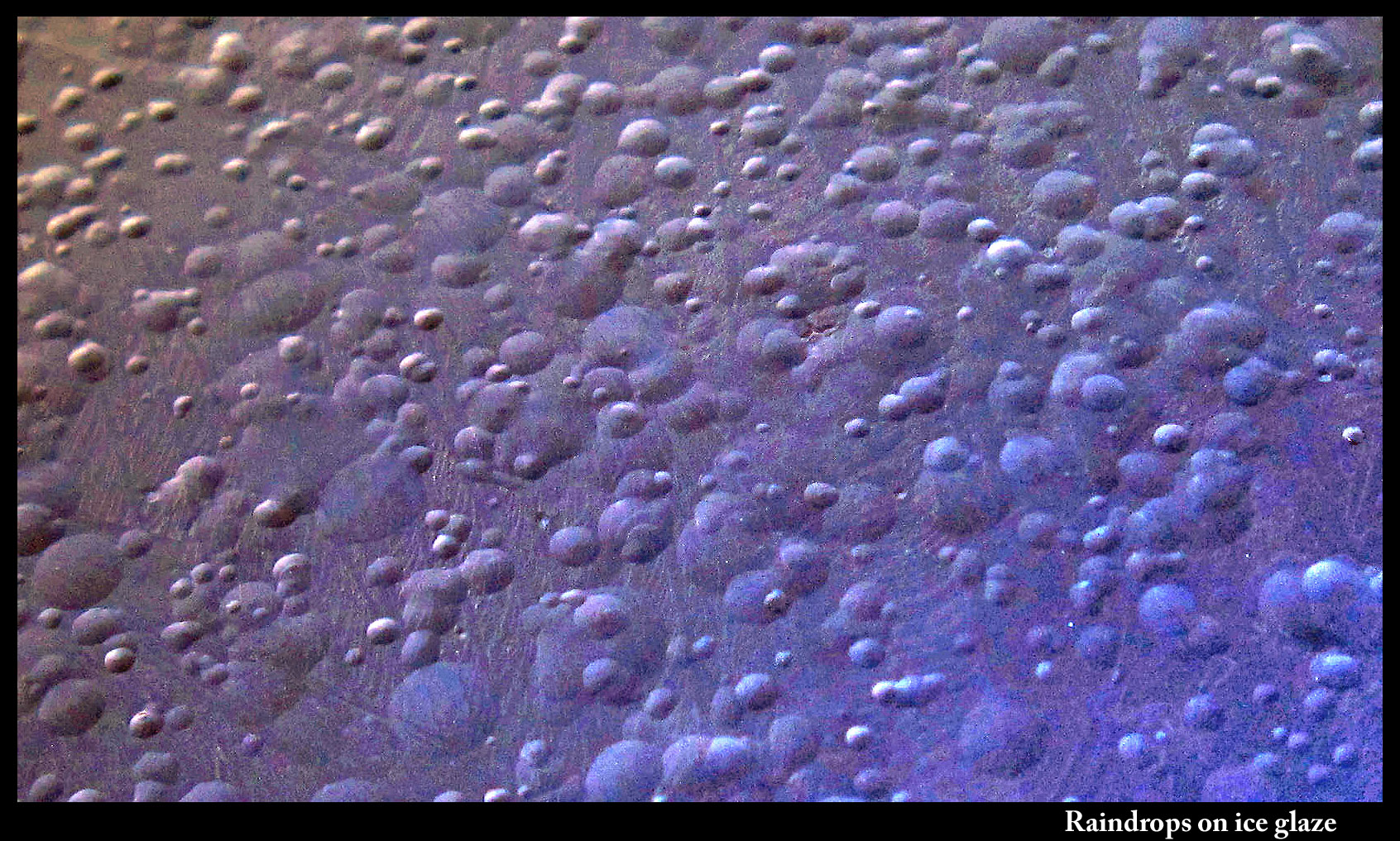
Raindrops on ice
February 23rd, 2014When water droplets land on ice, what happens?
If the ice is at least several degrees below zero (celcius), the drops freeze quickly, and build up a whitish, bumpy surface.
When the ice surface is heated to melting, the droplets vanish into the melt.
When the ice is instead very close to zero, the droplet spreads out, but not completely. You can still see the boundary of the droplet.
In the early 90s, there was some scientific debate about the ice surface near zero. Some said it had a thin, liquid-water surface, a layer that allowed us to ice-skate and make snowballs. Others said that if that were the case, then a droplet placed on the ice would spread out and vanish. Experiments showed the droplets didn't vanish. The jury is still out on the nature of the ice surface.
-JN
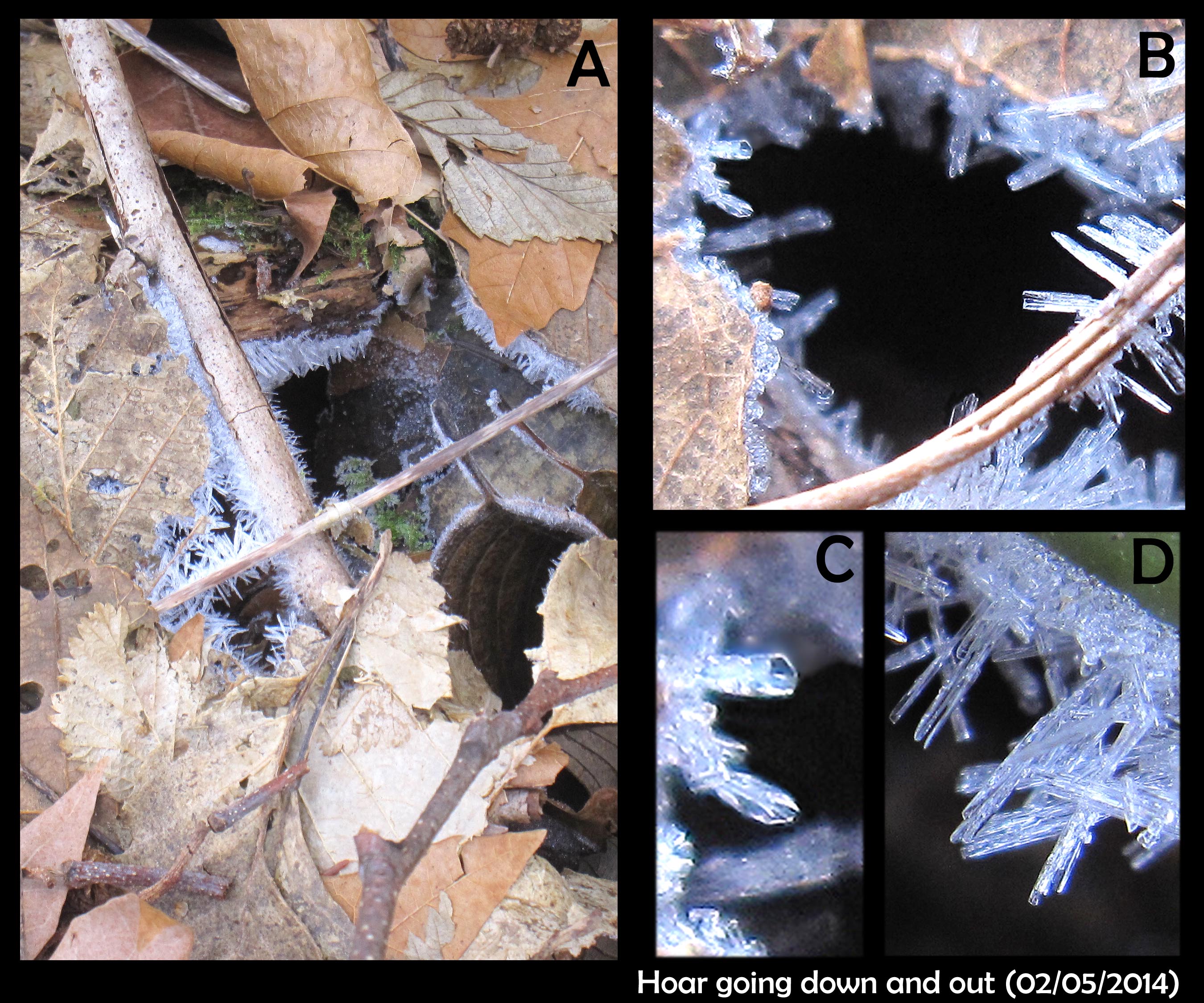
Hoar that grows down and out
February 9th, 2014It had been a continued spell of cold days and nights, the ground snow-free, the air clear and dry. No film-frost on the cars in the morning, and no spikes of hoar frost sticking up on grass or post. The only signs of ice had been the frozen pond and the needle ice, making the ground crunchy underfoot.
And yet in the woods and lawn, hoar frost still lurked.
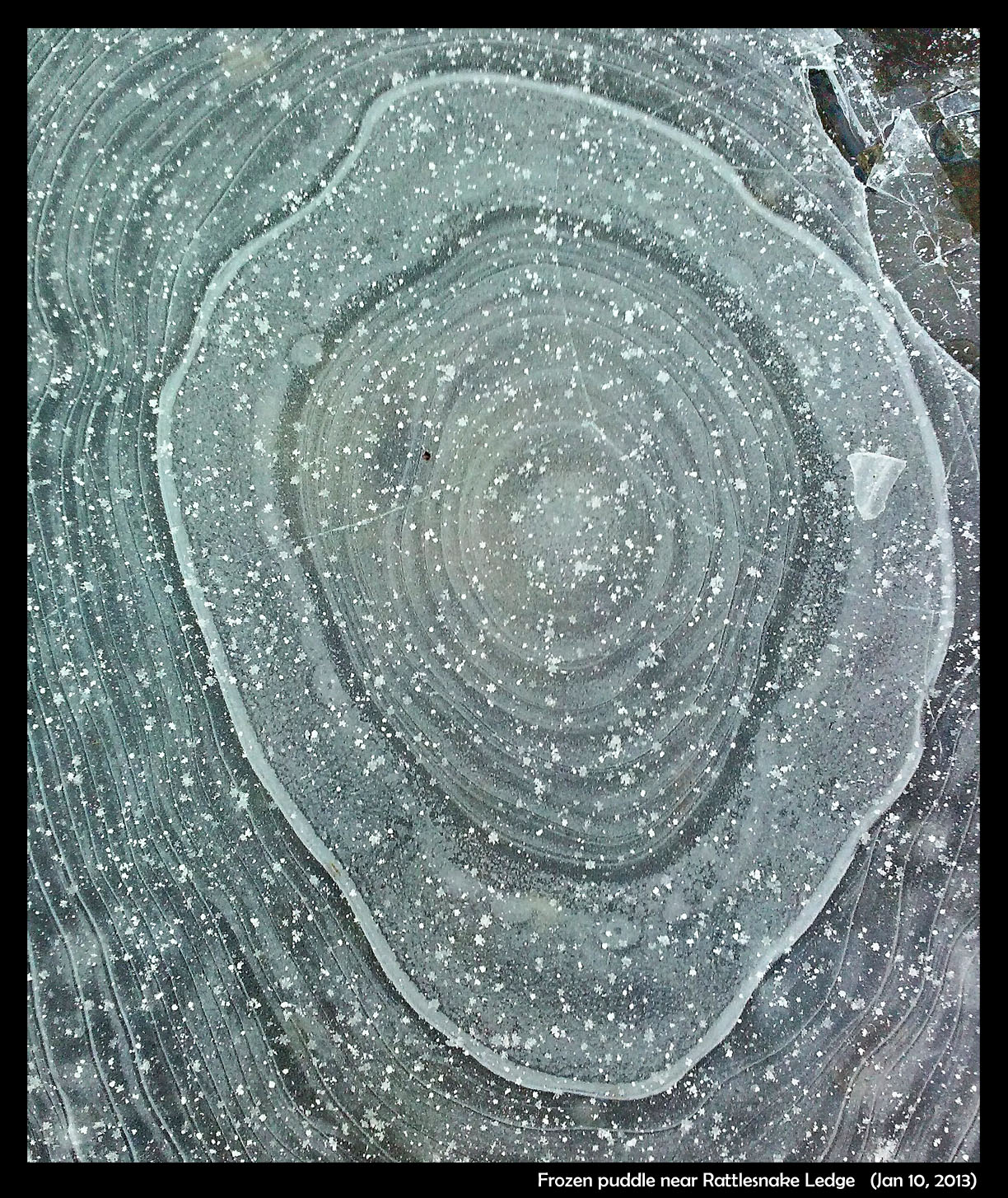
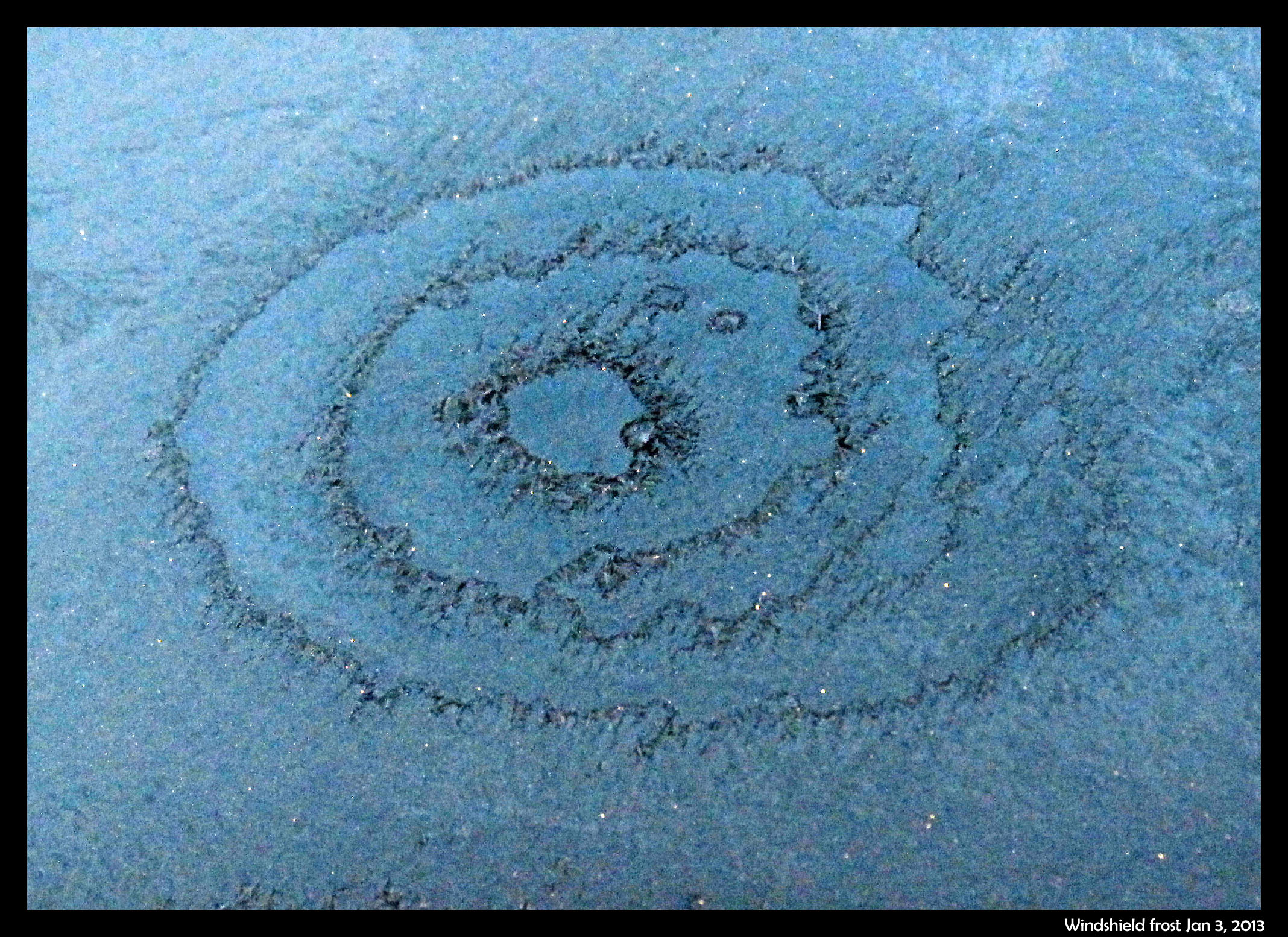
What makes the thick curvy lines in frozen puddles?
January 27th, 2013My sister recently sent this photo of a frozen puddle, a little over a foot across. Something broke out a piece of ice in the upper right, but it’s mainly a complete glaze over the top. (The white dots are rimed snow crystals. Click to zoom in and see.)
Notice how it has drained – the light color is due to the air underneath. The lines are roughly concentric with the shape of the puddle, though there can be considerable variation. On larger puddles or ponds, you might just see these thick curvy lines just near the shoreline.
Rime falling from branches
January 24th, 2013While riding my bike home the other day, I saw what appeared to be a patch of light snow.
It was the only such patch around. Looking closer, I could see that it consisted not of snow, but of chunks of partly melted rime deposits. (Note how the pieces are long and narrow, like little icicles.)
Just above were the branches of a huge Douglas Fir tree. Perhaps there had been an over-active squirrel or two up there. Other trees still had their rime. Hard to see why only this tree would have its rime fallen off.
- JN
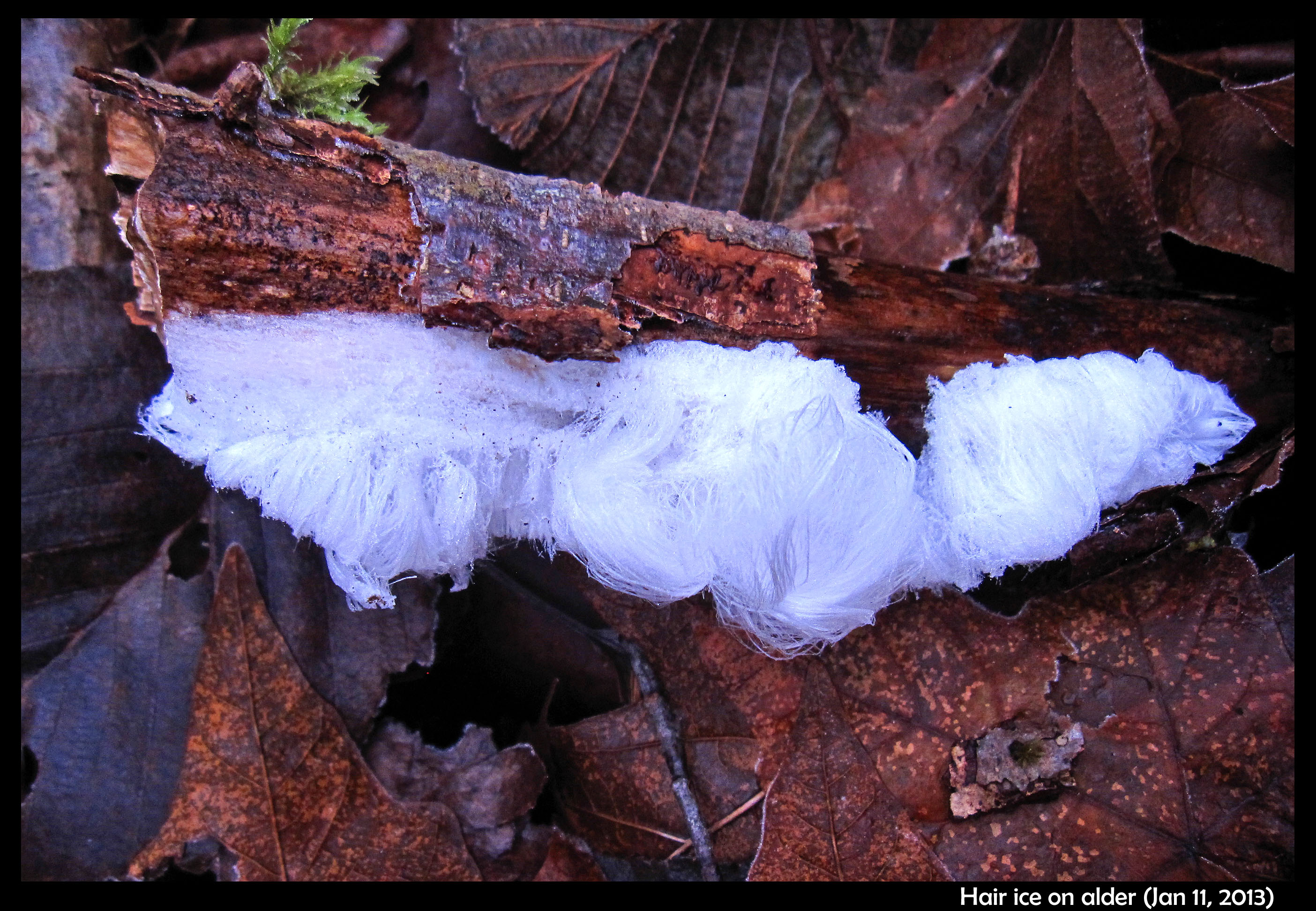
Hair Ice on Wood and Pavement
January 16th, 2013The morning after a rapid cool-down, I found hair ice on an alder log.
From a distance, it looked unnaturally white, like it was a bit of discarded cotton or white paper, but the closer I got to it, the more incredible it seemed.
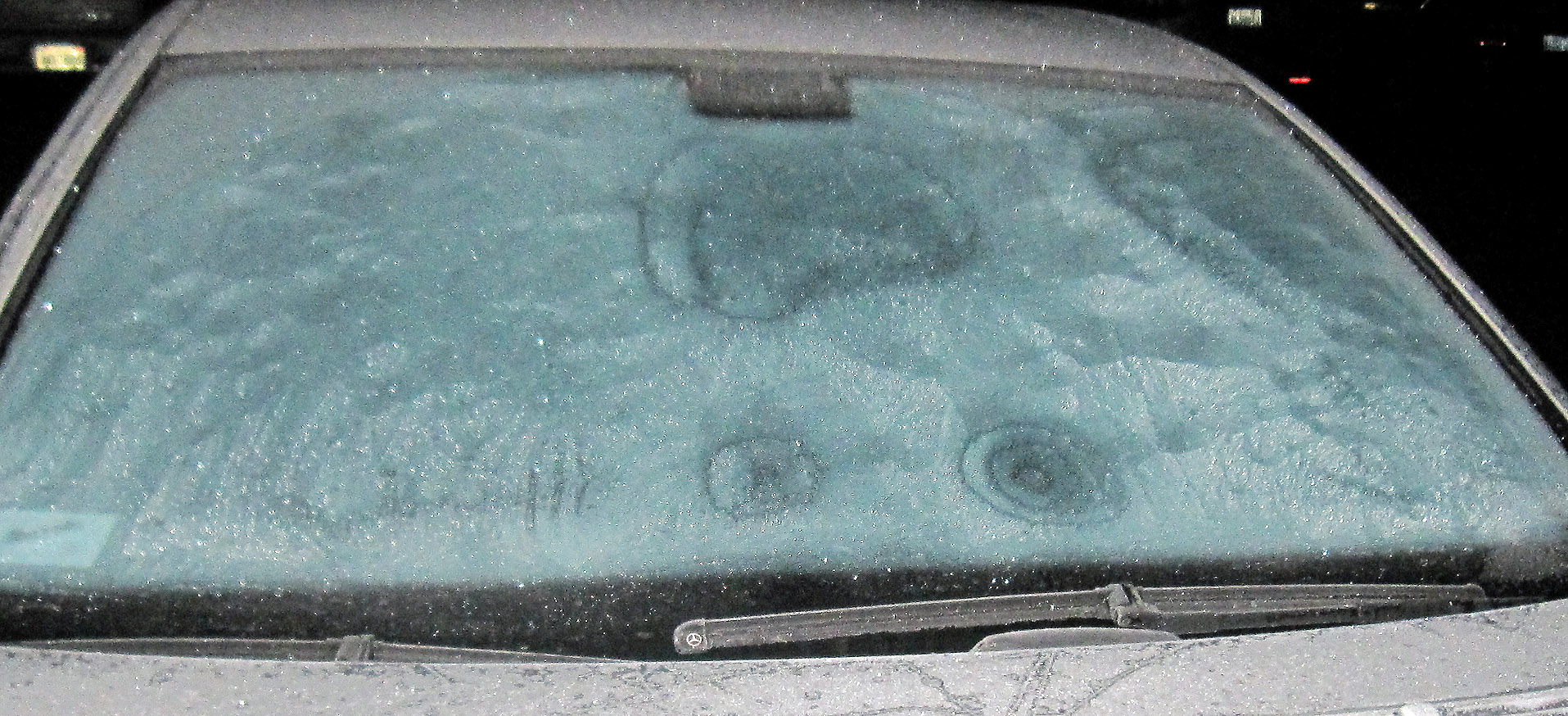
Crystal-to-crystal “communication” through vapor and heat
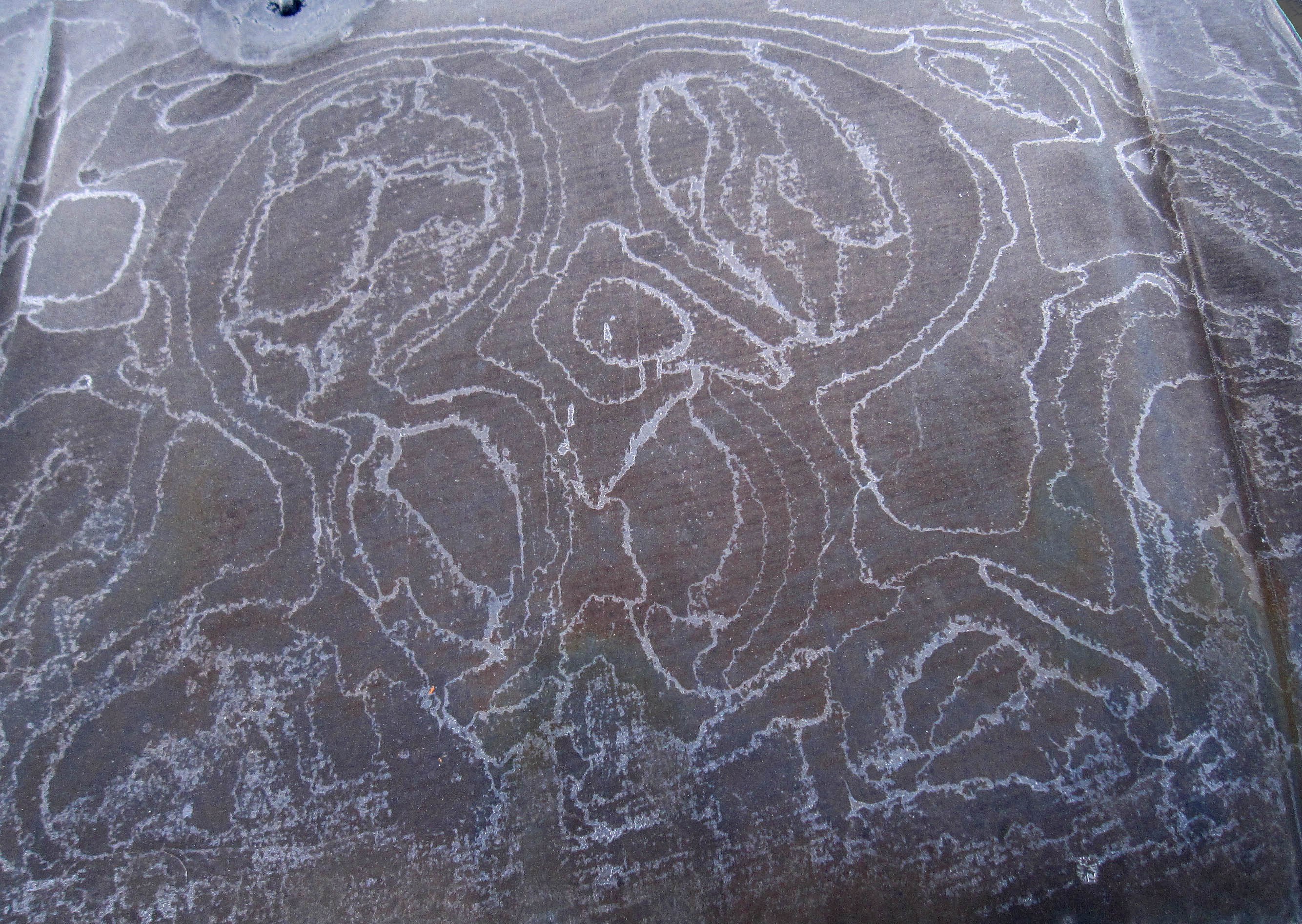
January 5th, 2013Two mornings ago, I saw this on the windshield of a parked car.
The bulls-eye pattern wasn’t centered on any particular feature on the windshield, and there were similar, though less developed, patterns nearby. See them on the photo below.
The dark parts are largely frost-free regions, and thus are regions that dried out during the crystallization event. (It was still dark when I took the shots.) Later, under a brighter sky, I saw a different pattern on the hood of another car, a pattern that I figure has a similar cause. In the hood case, shown below, the dry regions are bright due to reflection of the sky.
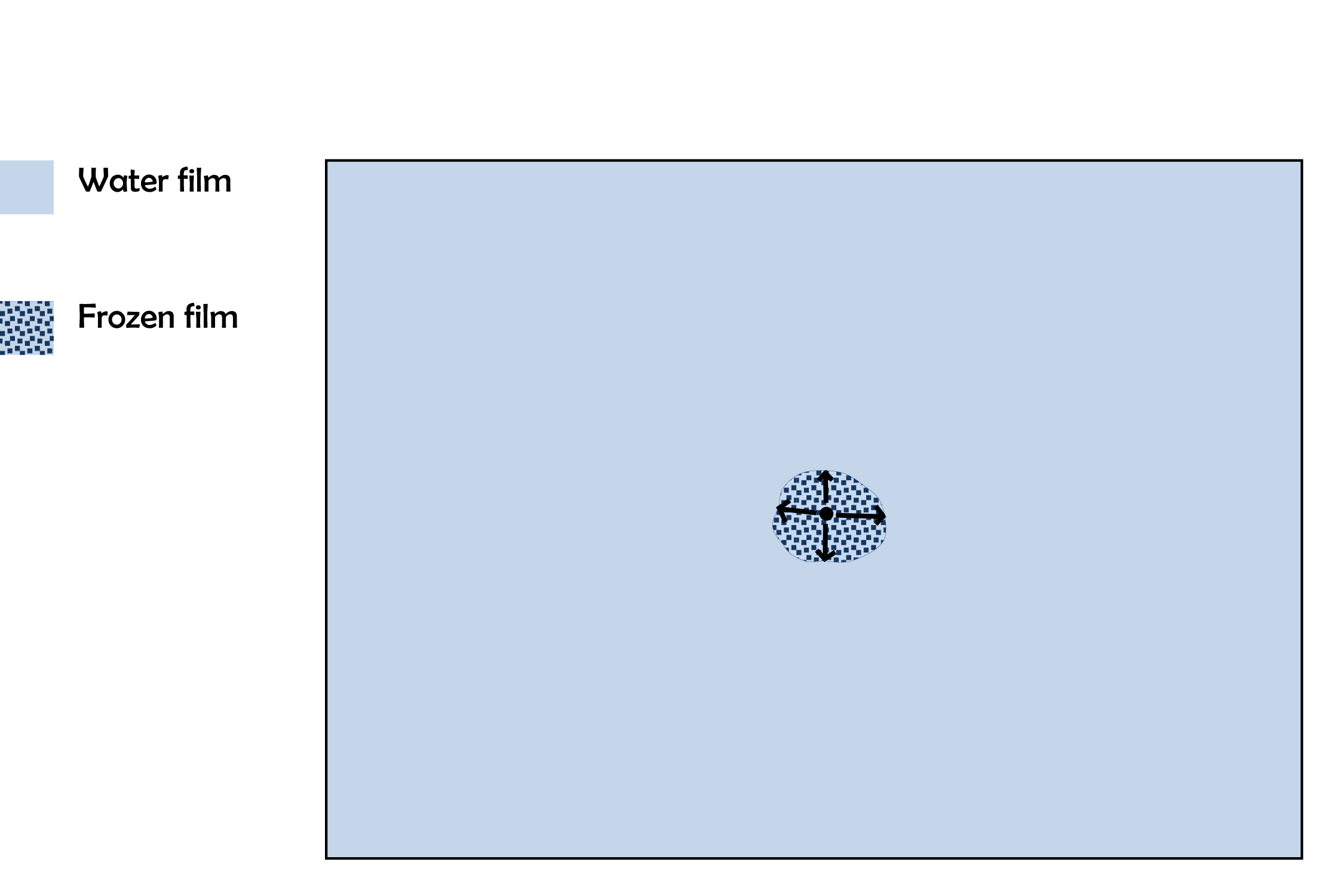
Now, about those concentric rings …
I puzzled over a larger such pattern in the Feb. 5, 2010 posting “Ripples”. The causative process that I proposed back then seems consistent with this newer observation, but I will clarify it here.
Before the first frost formed, the windshield, though seemingly dry, nevertheless had a thin layer of liquid water. This thin film had cooled to some temperature below freezing. (See the sketch “How hoar frost forms” in the Jan. 11, 2012 posting.) As the windshield and water film continued to cool, freezing was inevitable; the only issue was where. The first such spot to freeze must have had some feature, however minute, that was advantageous to freezing. It may have been a nucleant particle (e.g., a mineral dust grain, a type of bacteria, or even a tiny fleck of ice that wafted in from somewhere else), a slightly cooler spot, or a slightly thicker water film (e.g., from a scratch or indentation). But for whatever reason, the ice formed there first.
Now suppose the ice spreads outward from the nucleation spot in all directions with about the same rate. I suspect this happens when the film is extremely thin, as it would have been under the relatively dry conditions of this day. So, the frozen film grows outward, roughly as a disc. See the sketch below; the black dot in the center is the first place that froze.
Trip of the Ice Man
November 9th, 2012
The "Ice Man" -- that's how a newspaper header referred to me after I gave a recent conference lecture:
A link to the article is here:
http://www.sctimes.com/article/20121023/NEWS01/310230011/Featured-speaker-details-snow-crystals-SCSU-storm-conference
It was a very enjoyable visit to the 7th annual Northern Plains Winter Storms Conference on the campus of St. Cloud State University in St. Cloud, Minn. We had various talks including one about forecasting a storm, the statistics of the snow-to-liquid equivalent ratio (e.g., in some areas about 13" of snow will melt to 1" of water, but regions and storms vary considerably, some being over 70 to 1),and one talk about how a late-season snowstorm might end a locust plague (unlikely, according to the speaker).
My talk described how a simple principle allows us to understand how a wide variety of snow crystal forms originate.
Here's the narrated talk. To view, click the image, then enlarge to full screen:
">
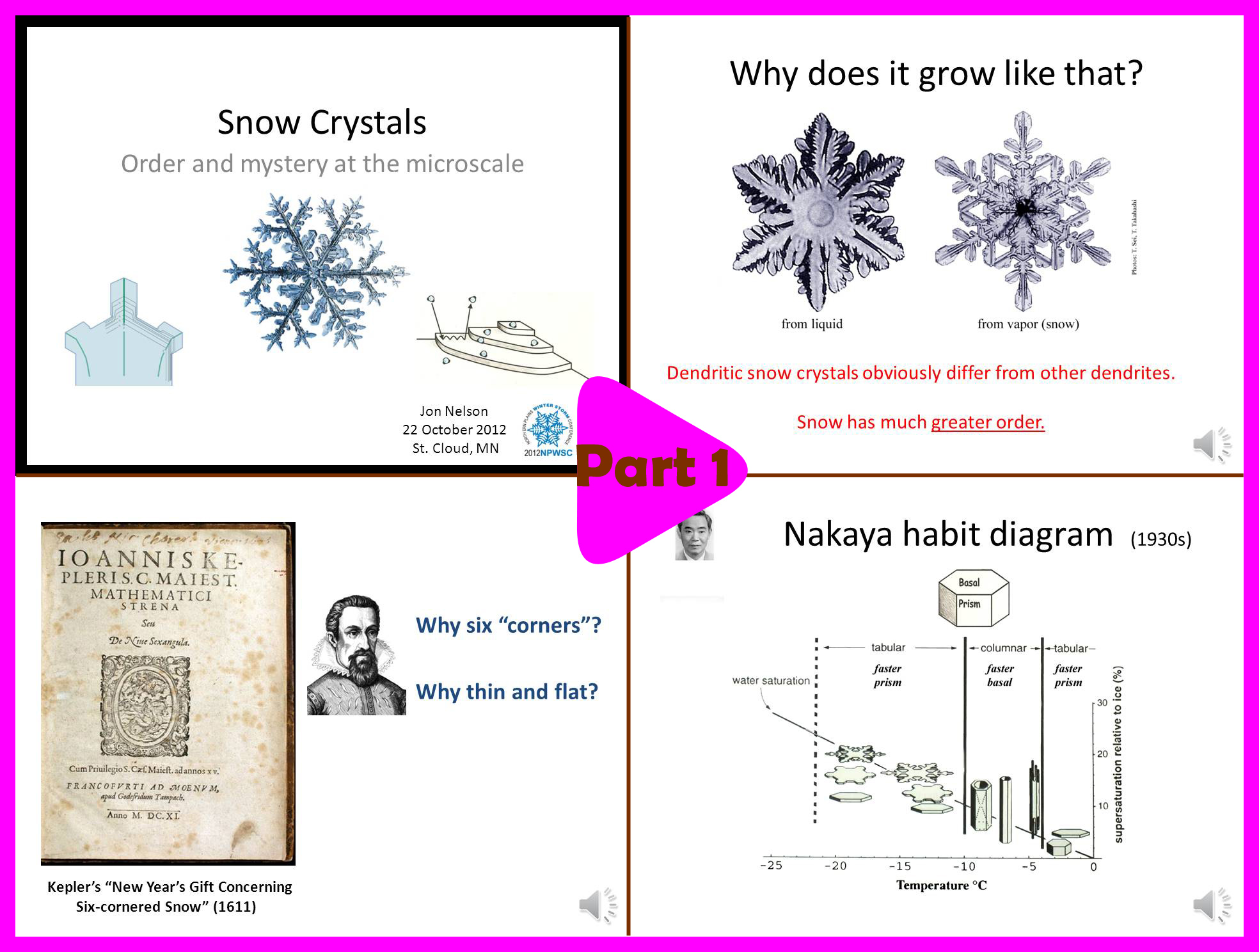
Part 1 (10 min):
-> Why study snow crystal shapes?
-> Some history about snow science.
-> The habit map.
-> Questions that will be answered in the rest of the talk.
">
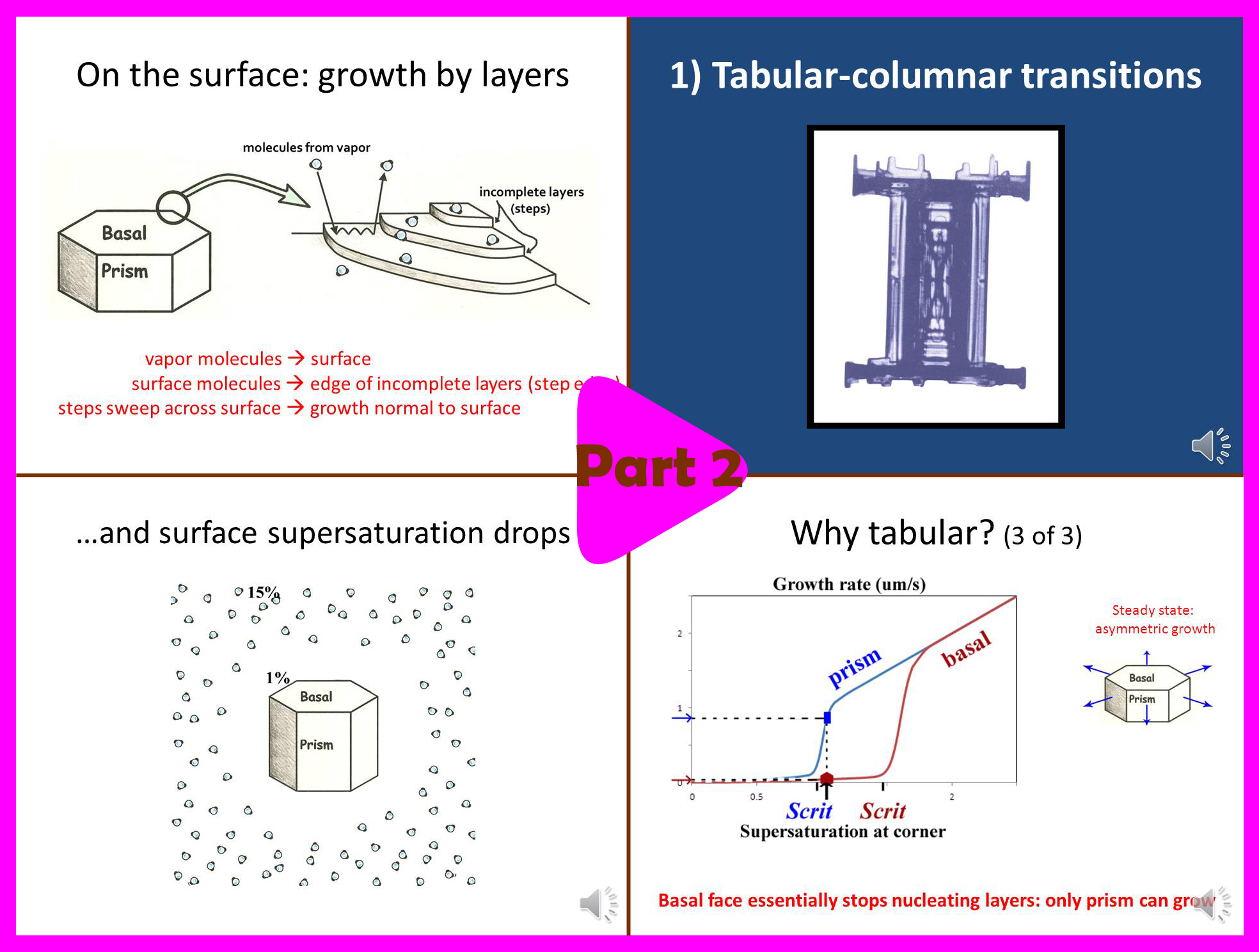
Part 2 (13.5 min):
-> Basics of snow crystal science.
-> Why dendrites grow so thin.
-> Why needles and columns sometimes form.
">
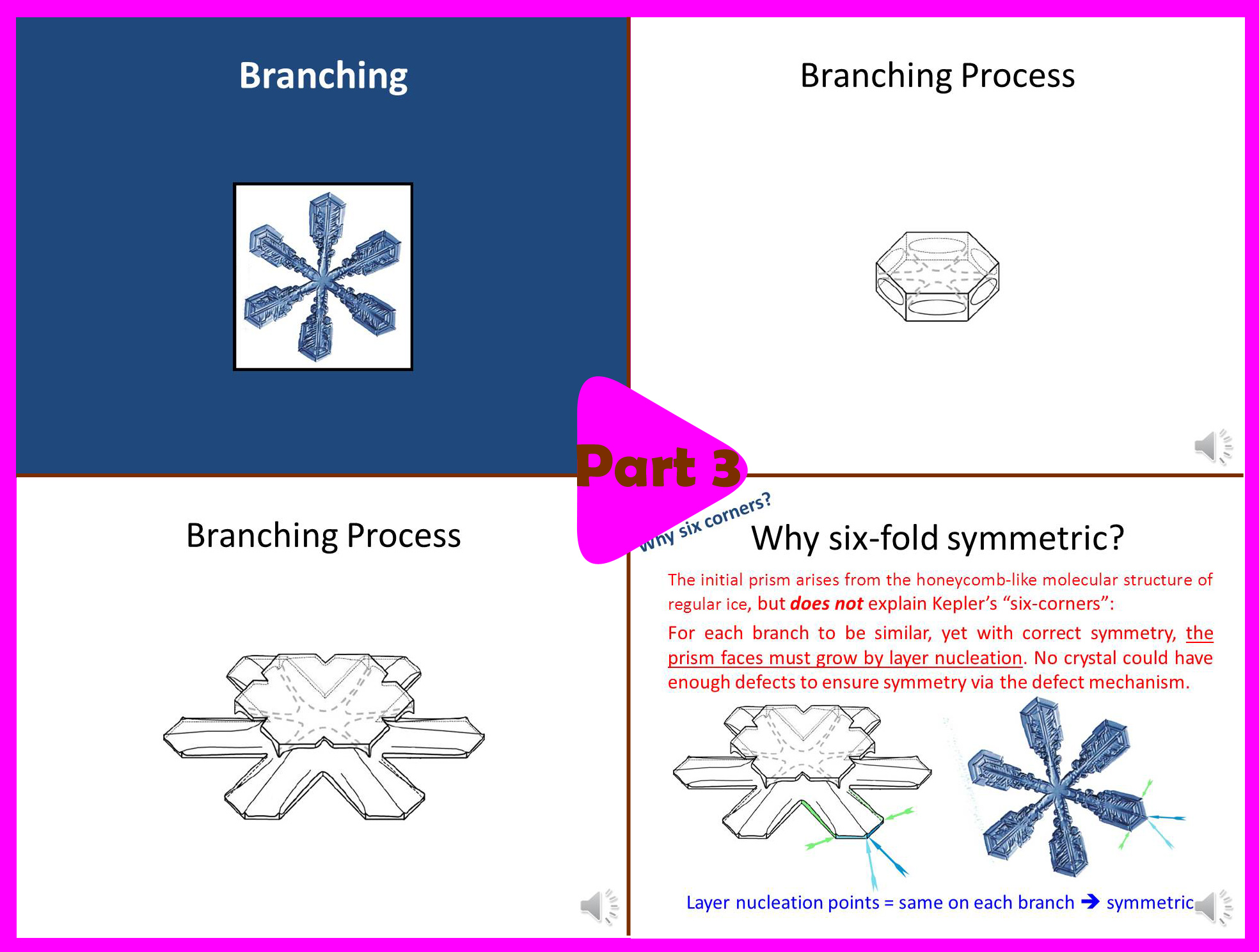
Part 3 (6 min):
-> How the crystals get their branches.
-> Why they are six-fold symmetric.
">
Part 4 (14.5 min):
-> How the crystals get sidebranches.
-> Common errors we make when drawing snow.
-> Why they have so much variety.
-> Mysteries about snow.
-> What are the "messages in water".
It is a scientific talk, so it involves some diagrams and technical terms. But this one is pretty easy. Perhaps the only technical terms are "vapor deposition" and "supersaturation". Vapor deposition happens when water molecules in the air (i.e. water vapor) crystallize onto something, like a snow crystal or hoarfrost. The vapor must be "super" saturated for this to happen. Greater supersaturation means greater vapor density and thus faster growth. The above link goes to the first segment, and from there you can click on the subsequent segments.
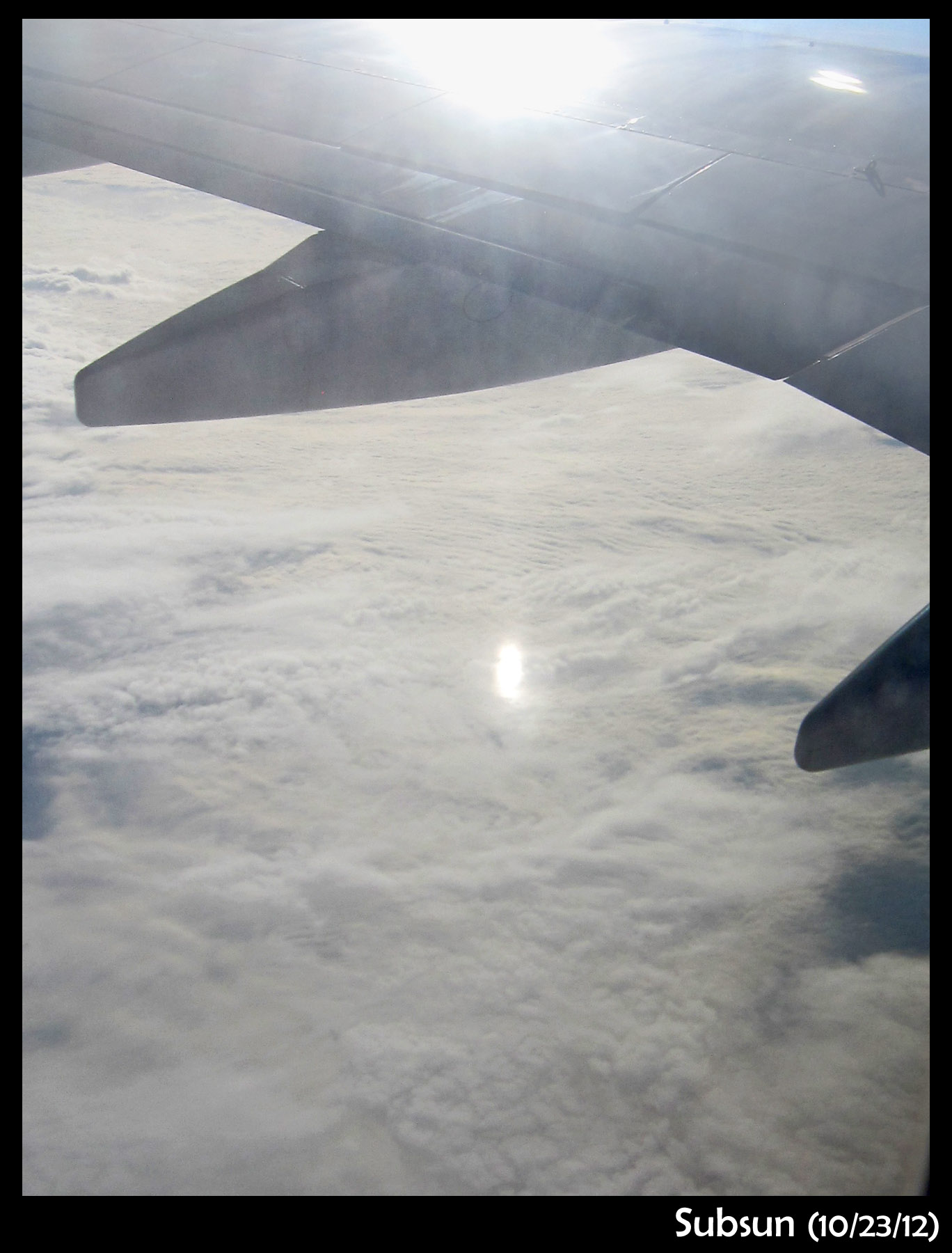
On the flight home, I saw a subsun on the clouds below. A subsun is a reflection of the sun from tiny, flat, hovering plate-like (tabular) ice crystals. They are essentially hovering like microscopic flying saucers.
In the photo above, you can see the sun's reflection off the wing on top. The smaller reflection on the clouds below is the subsun. I used to think the subsun was rare, but apparently I simply wasn't looking. This subsun was there in various forms for at least 2/3rds of the flight. I've seen them on most previous flights. More on subsuns in the next post.
- Jon
Here's the abstract to the talk:
snow crystal seminar abstract.pdf
And here are the four parts of the talk in pdf form (from the PowerPoint slides):
snow order and mystery - 1of 4.pdf
snow order and mystery - 2 of 4.pdf
snow order and mystery - 3 of 4.pdf
snow order and mystery - 4 of 4.pdf
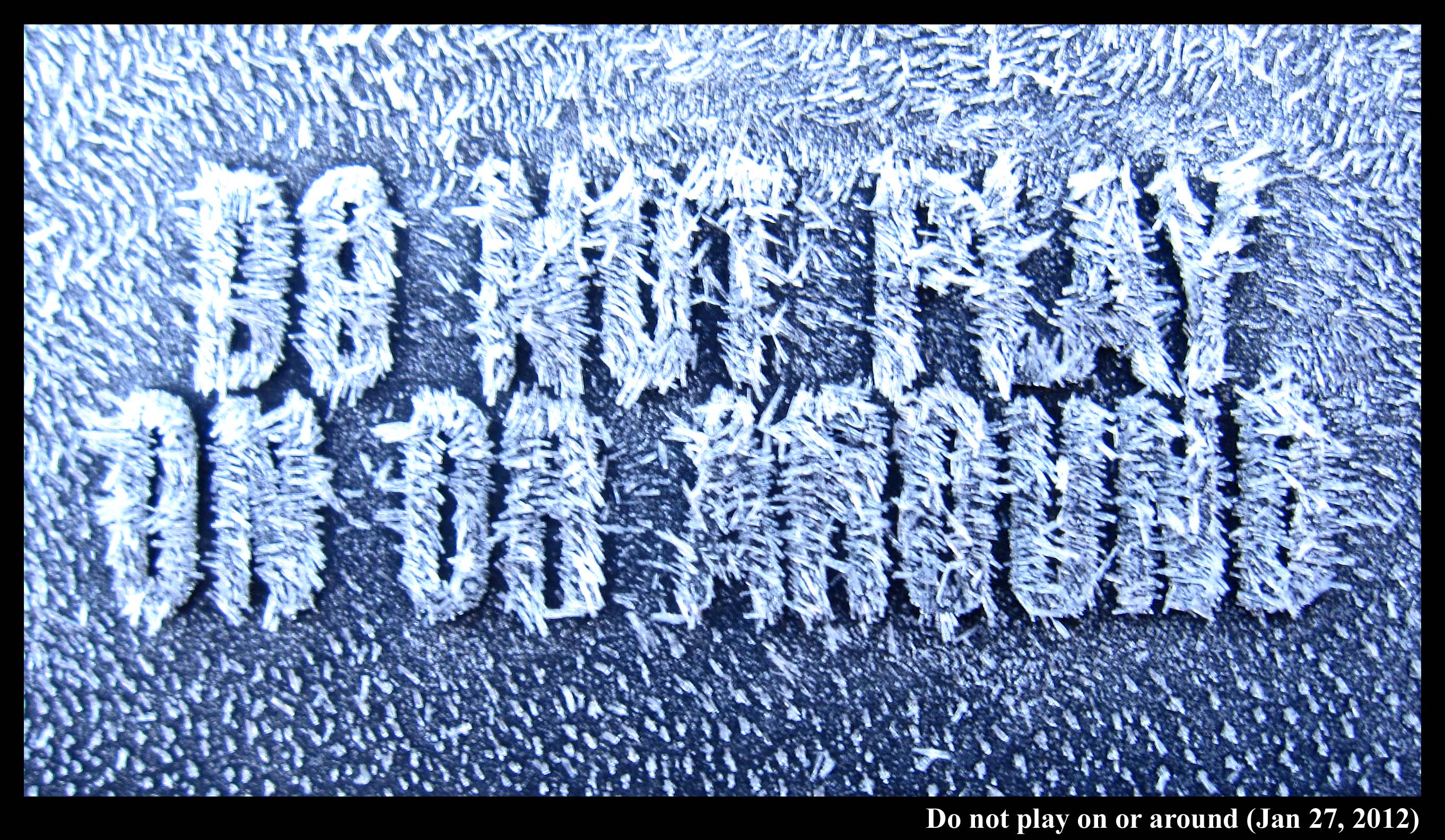
Caution!
February 1st, 2012Hoar. It's just a white coating on things, so why does it make everything look more interesting?
I saw this hoar coating on a plastic trash-can lid:
The hoar frost on the lid had various whirls, just like I've seen on the plastic surfaces of car door handles and side-view mirrors. This hoar was a little different though in that the crystals were definitely sticking up and not laying flat on the surface. Nevertheless, the fact that they show a pattern at all, and are not just randomly oriented, means that there must have been a liquid film of water that first froze to the surface. The film froze, producing a pattern of crystal orientations on the surface, and these orientations were not revealed until the hoar frost grew. Hurray for hoar!
Here's another warning:
The hoar crystals are longer on the raised lettering, particularly near edges. This is not because such places are further from the ground, but because they have more radiative cooling (due to their more expansive view of the sky) and can stick out into regions with a greater density of water vapor molecules.
If you click on the images, you can see the crystals a little better. But I forgot my tripod on this particular morning (I took the shots after I got to the office), and so the images aren't as crisp as my other close-up shots.
- Jon
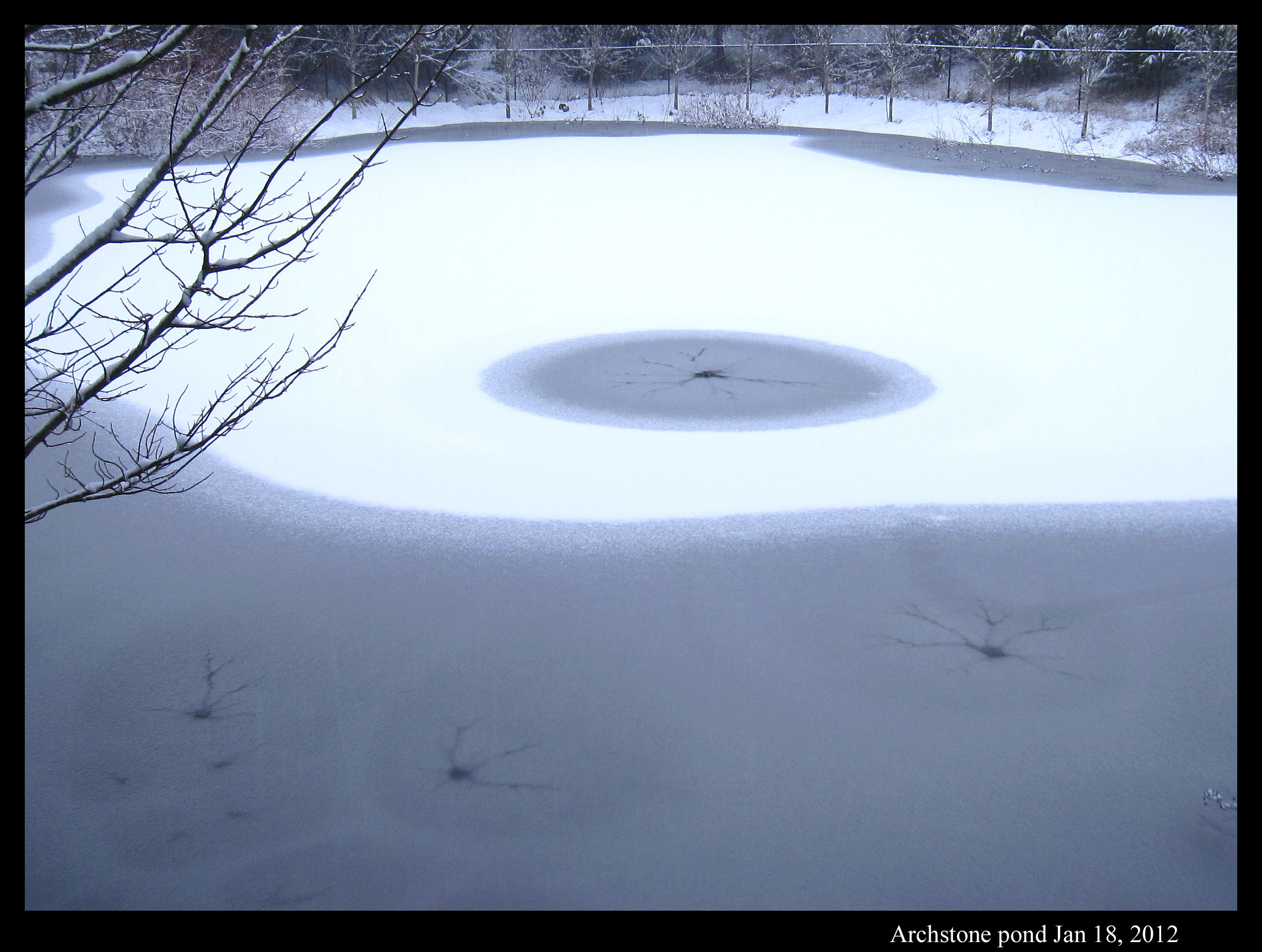
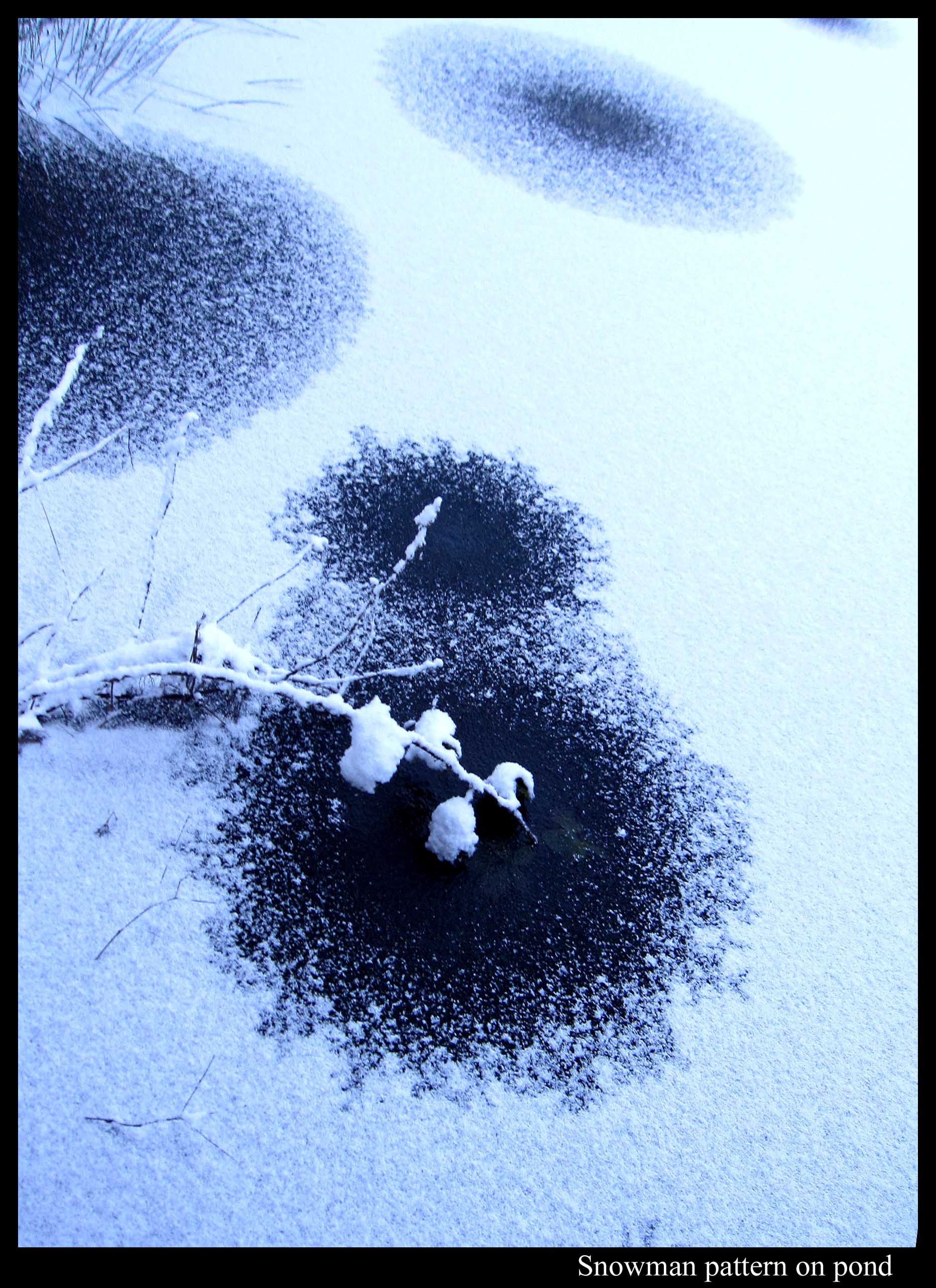
Slush Fingering and Other Pond Patterns
January 19th, 2012Here in the Pacific Northwest, we just had our first snowfalls of the season. On the weekend, we had 1 – 2 inches. This was followed on Wednesday by what the Seattle Times newspaper was calling a “megastorm”. But in the end, most areas in the area got only a few inches. Here in Redmond, we had 4 – 5 inches. And though the temperature barely dipped below freezing, I had several opportunities to observe snow patterns on the neighboring pond.
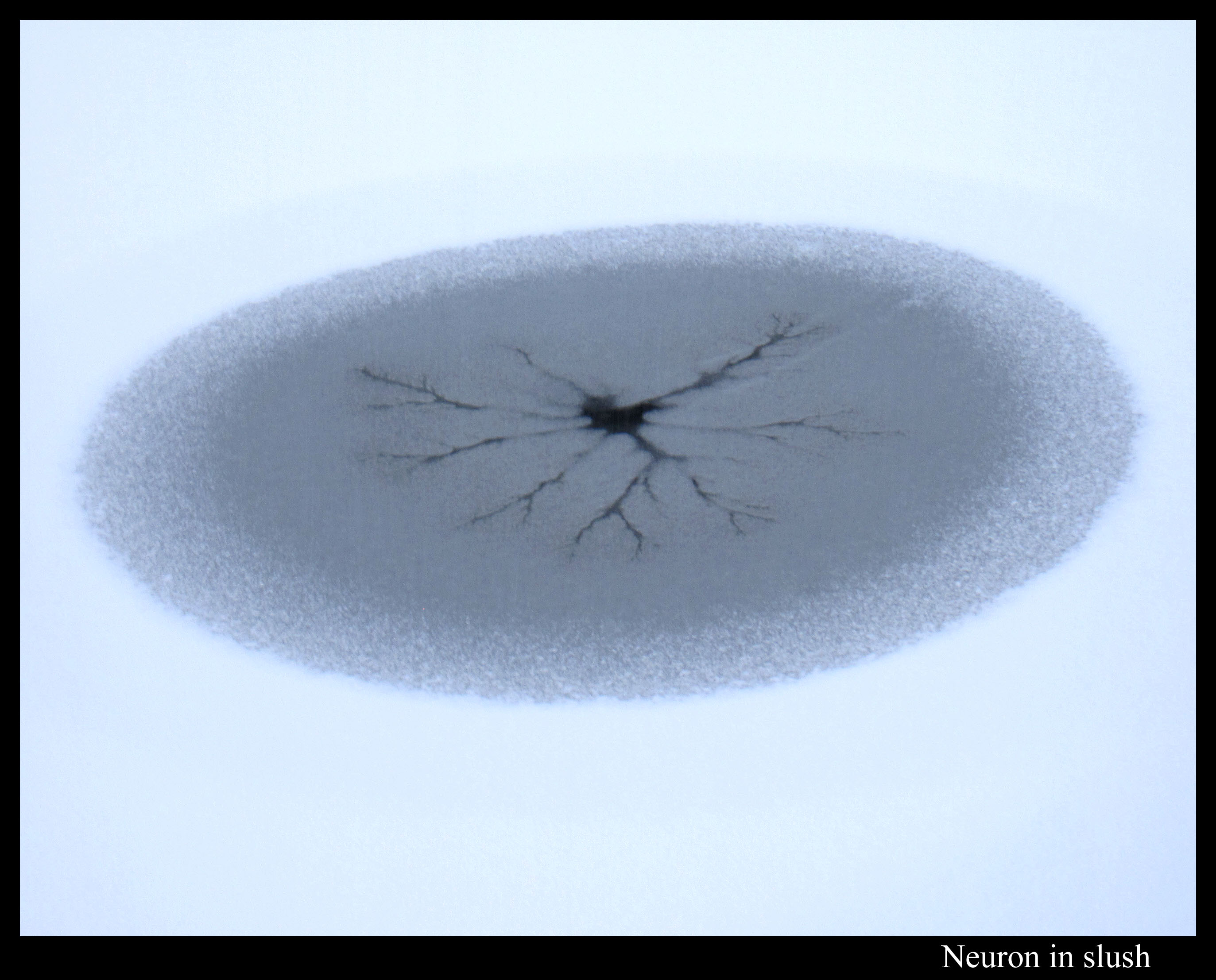
Or maybe I should say slush patterns. (Slush is a roughly uniform mixture of water and snow or ice.) Take the viscous fingering pattern I mentioned in my pond-ice post of a few days ago. Here is a similar type of pattern, except this looks like a neuron dendrite inside an egg.
Unlike the Boulder ice in that previous post, the ice layer on this pond was way too thin for me to walk on. Perhaps that’s a key to understanding why the patterns here instead had darker regions near their center. I don’t know. Anyway, the pond had a few such regions in which the water created dendrite-like fingering.
On the first snowfall, the pond had more circles with dark centers, but perhaps because the amount of snow was less, there was no discernable fingering near the centers, just dark centers caused by more uniform flooding.
In general, the basic layering was liquid below, clear and solid ice above, slush (or frozen slush) on top of the ice, and snow on top of the slush. (There can also be slush under a layer of solid ice.) The first snowstorm, though it had less snow, was preceded by colder weather. So, the clear ice was a little thicker and the slush layer thinner. Between the snowstorms, the ice melted and for awhile we had just slush on top of the liquid water.
The circular and fingering patterns arise when water gets pressed out of a small hole in the ice. The water then floods the ice as sketched below.