Category: "Snow Science"
Trip of the Ice Man
November 9th, 2012
The "Ice Man" -- that's how a newspaper header referred to me after I gave a recent conference lecture:
A link to the article is here:
http://www.sctimes.com/article/20121023/NEWS01/310230011/Featured-speaker-details-snow-crystals-SCSU-storm-conference
It was a very enjoyable visit to the 7th annual Northern Plains Winter Storms Conference on the campus of St. Cloud State University in St. Cloud, Minn. We had various talks including one about forecasting a storm, the statistics of the snow-to-liquid equivalent ratio (e.g., in some areas about 13" of snow will melt to 1" of water, but regions and storms vary considerably, some being over 70 to 1),and one talk about how a late-season snowstorm might end a locust plague (unlikely, according to the speaker).
My talk described how a simple principle allows us to understand how a wide variety of snow crystal forms originate.
Here's the narrated talk. To view, click the image, then enlarge to full screen:
">
Part 1 (10 min):
-> Why study snow crystal shapes?
-> Some history about snow science.
-> The habit map.
-> Questions that will be answered in the rest of the talk.
">
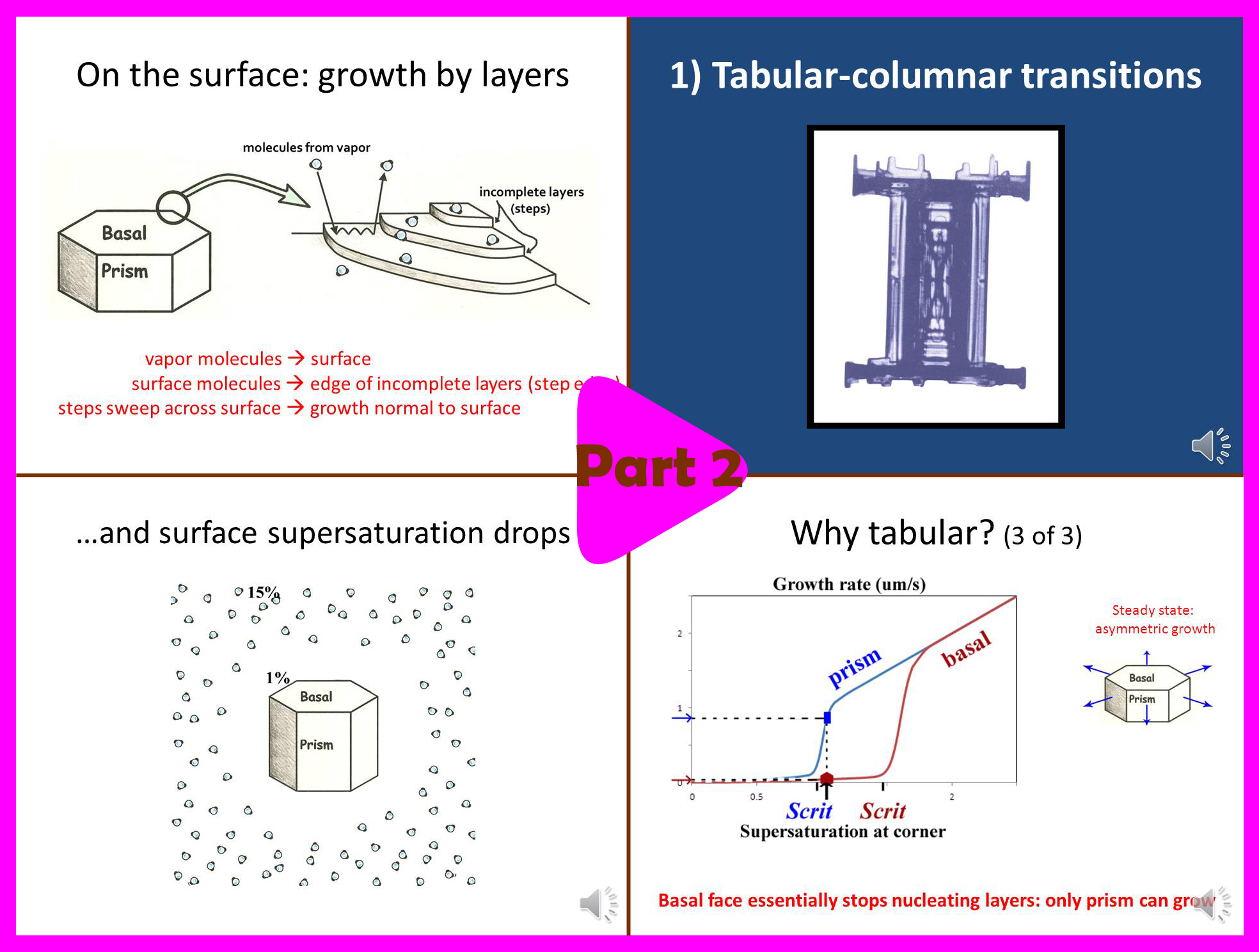
Part 2 (13.5 min):
-> Basics of snow crystal science.
-> Why dendrites grow so thin.
-> Why needles and columns sometimes form.
">
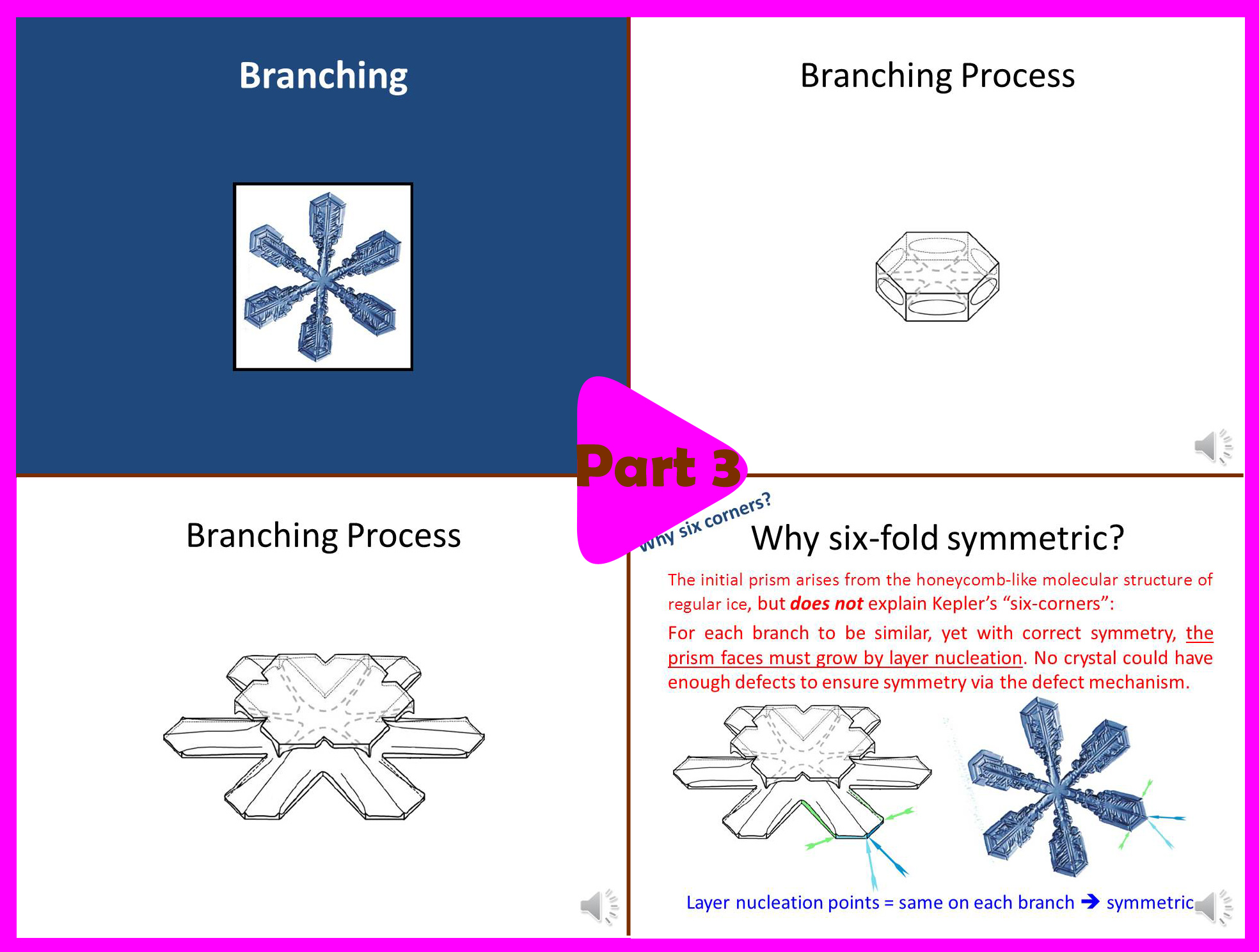
Part 3 (6 min):
-> How the crystals get their branches.
-> Why they are six-fold symmetric.
">
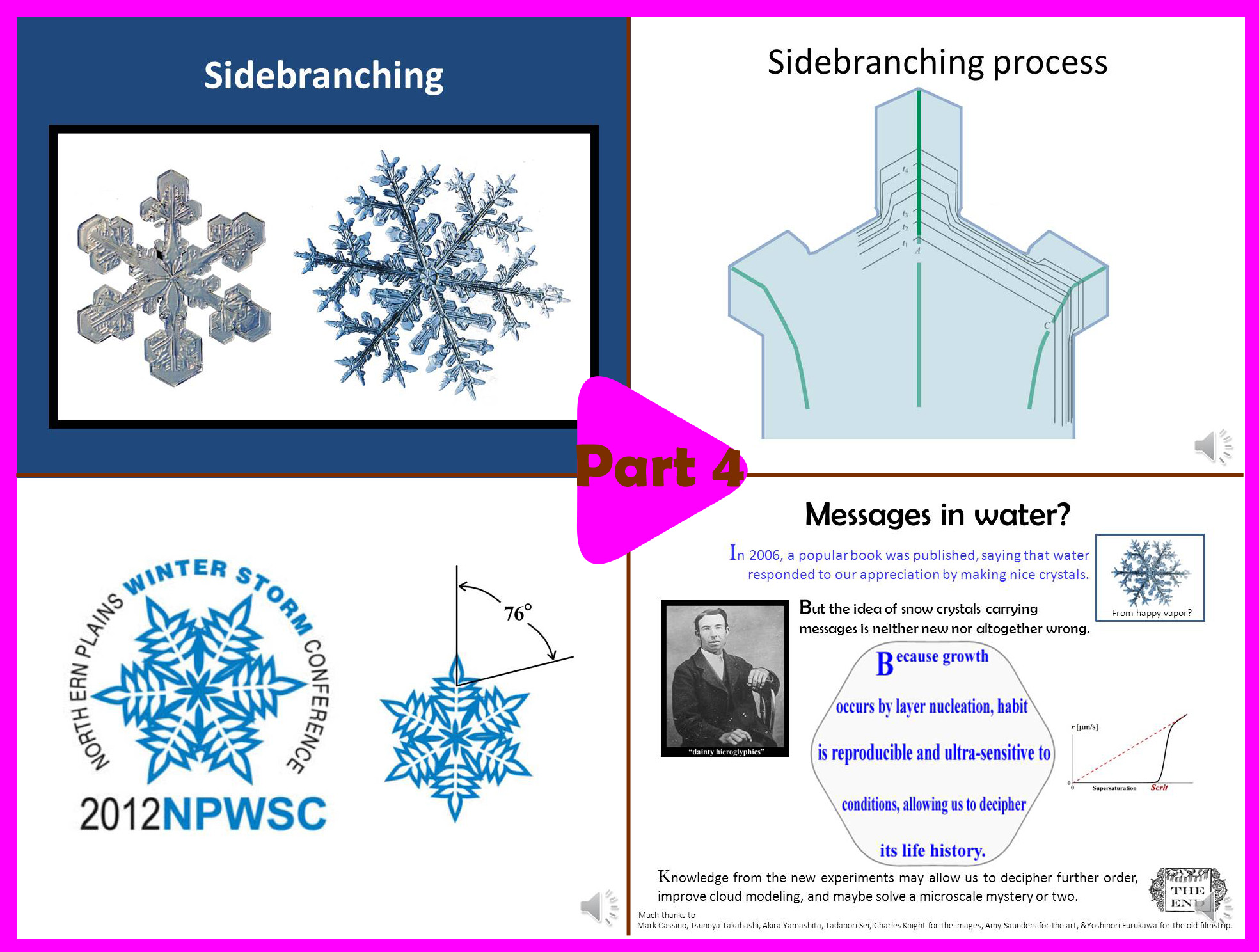
Part 4 (14.5 min):
-> How the crystals get sidebranches.
-> Common errors we make when drawing snow.
-> Why they have so much variety.
-> Mysteries about snow.
-> What are the "messages in water".
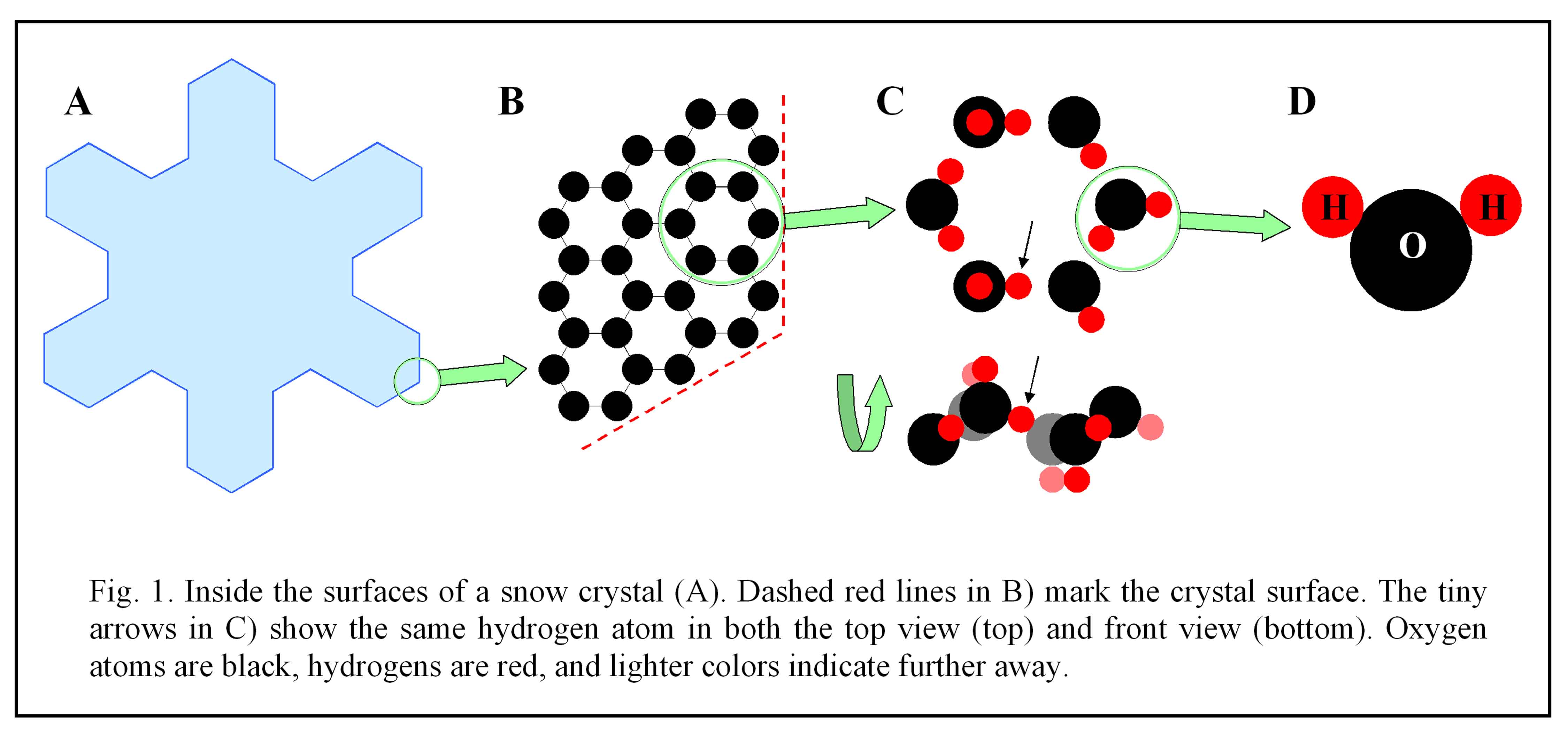
It is a scientific talk, so it involves some diagrams and technical terms. But this one is pretty easy. Perhaps the only technical terms are "vapor deposition" and "supersaturation". Vapor deposition happens when water molecules in the air (i.e. water vapor) crystallize onto something, like a snow crystal or hoarfrost. The vapor must be "super" saturated for this to happen. Greater supersaturation means greater vapor density and thus faster growth. The above link goes to the first segment, and from there you can click on the subsequent segments.
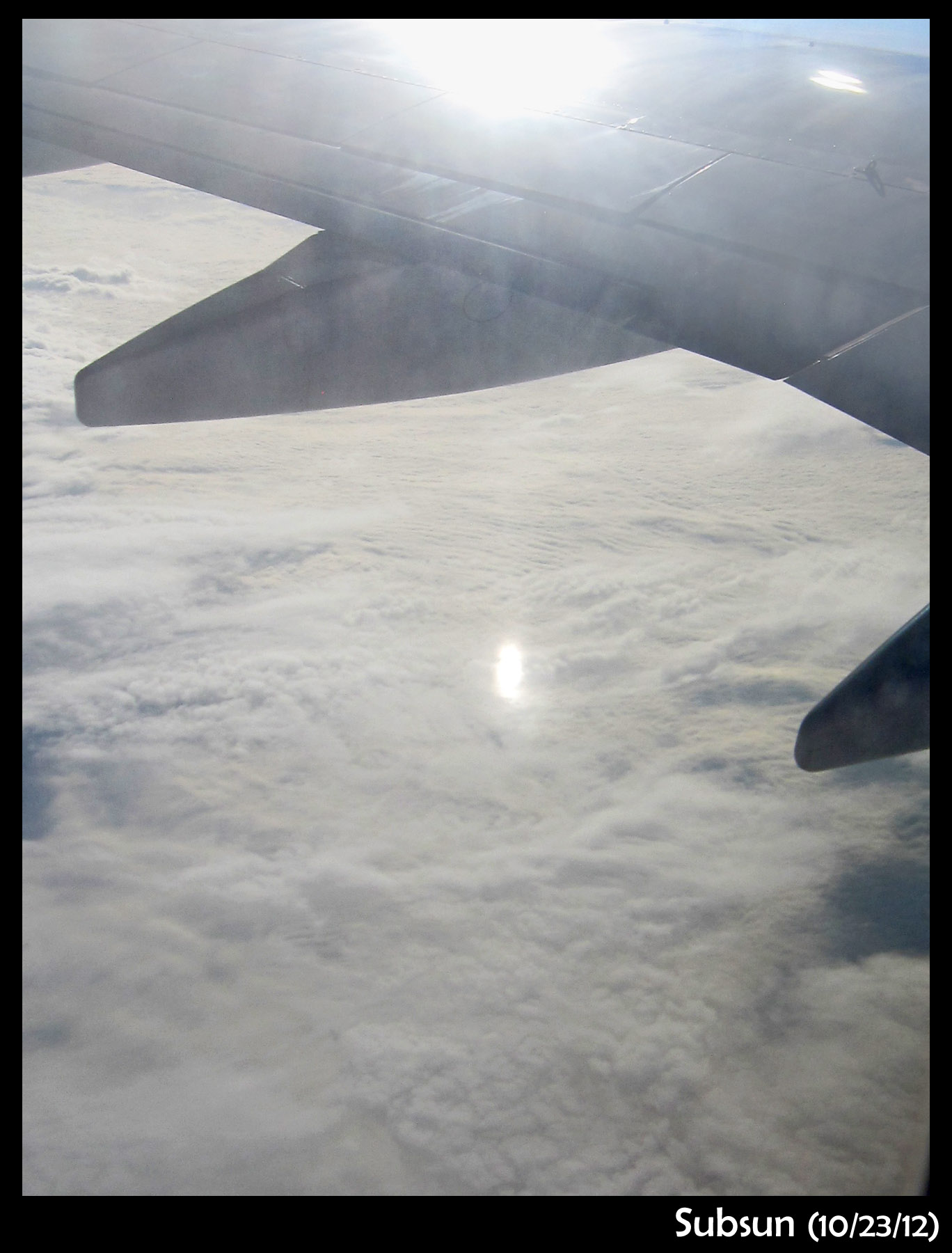
On the flight home, I saw a subsun on the clouds below. A subsun is a reflection of the sun from tiny, flat, hovering plate-like (tabular) ice crystals. They are essentially hovering like microscopic flying saucers.
In the photo above, you can see the sun's reflection off the wing on top. The smaller reflection on the clouds below is the subsun. I used to think the subsun was rare, but apparently I simply wasn't looking. This subsun was there in various forms for at least 2/3rds of the flight. I've seen them on most previous flights. More on subsuns in the next post.
- Jon
Here's the abstract to the talk:
snow crystal seminar abstract.pdf
And here are the four parts of the talk in pdf form (from the PowerPoint slides):
snow order and mystery - 1of 4.pdf
snow order and mystery - 2 of 4.pdf
snow order and mystery - 3 of 4.pdf
snow order and mystery - 4 of 4.pdf
Finally got it!
February 8th, 2012For a few years now, myself and another ice-researcher have been trying to get a research grant from the National Science Foundation to study snow. Well, we just recently heard that the funding came through and I’ll be starting on the project in March. Yeah!
You might wonder what it is that we don’t already know about snow. Well, the better question is, what do we really know? The answer is “not much”. There’s been a lot of experiments in the lab, spanning nearly 100 years now, with many interesting results, but nothing really clear has emerged. Here’s one of the basic problems: In a typical cloud consisting of supercooled droplets and snow crystals, we can calculate the crystal’s rate of growth fairly accurately if we know the crystal shape. But it is extremely difficult to predict the crystal’s shape, and the rate of growth can change a lot with the shape. That’s the thing about snow crystals - they come in a bewildering variety of shapes, and we still have no clue as to why. And if the crystal isn’t surrounded by supercooled droplets, the situation is even worse.
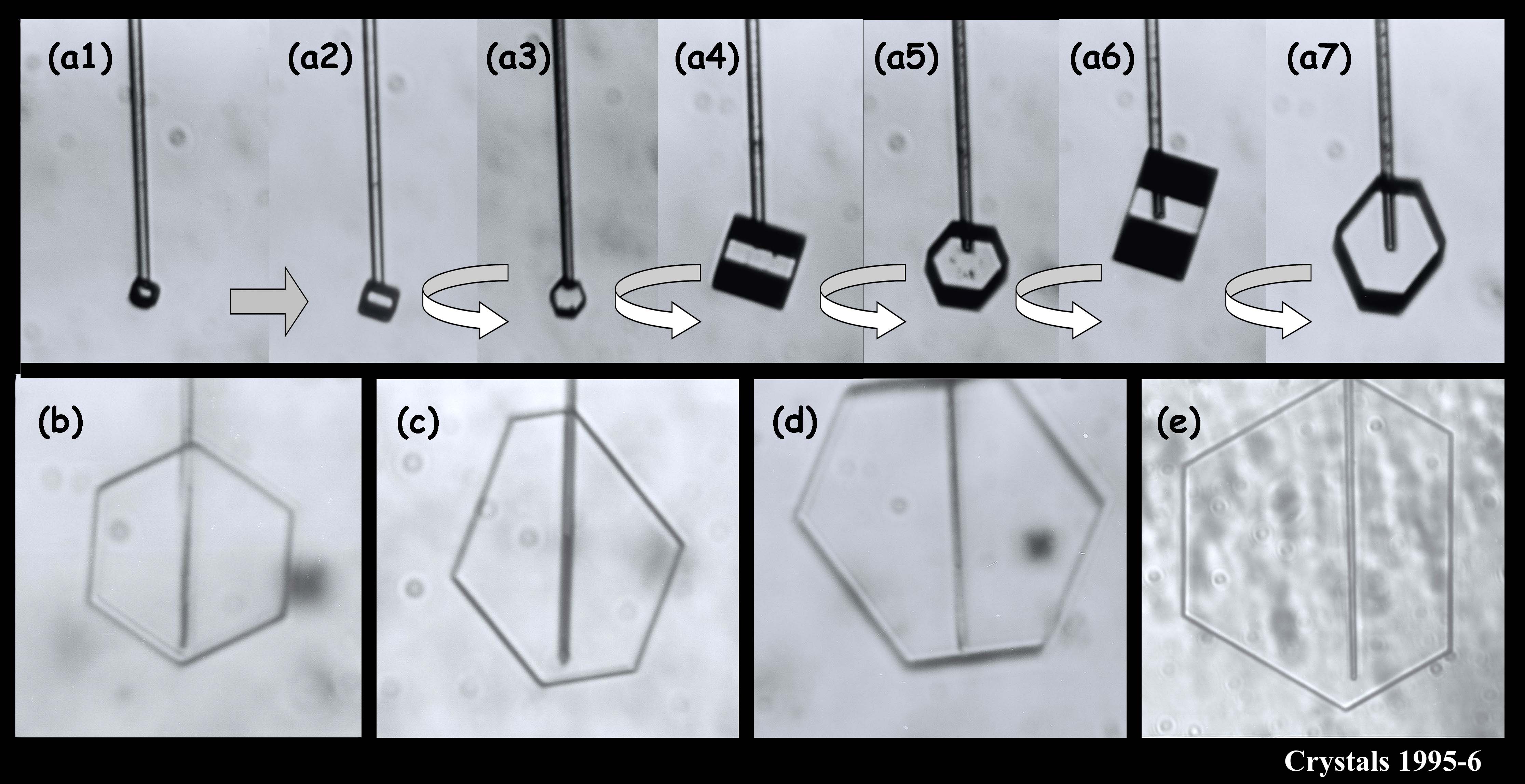
We argued in our proposal that the main reason we don’t have a clear picture about the development of snow crystal shape (and even growth rate) is because of problems with the experimental methods. Instrumental influences easily creep into the experiment and alter the crystal shape. We suggested a new method based on one I helped developed in 1994-1996. In that method, we grew single ice crystals from the tip of an ultrafine glass capillary (about 10x thinner than the typical hair on a person’s head). Some of the images below show what I mean about shape variety.
The crystals are all very small and compact because we were interested in growth with very low humidity. In the series (a1) - (a7), you see the crystal growing as I rotated the capillary to see all of the crystal faces. Sometimes I let a crystal grow for a week or more.
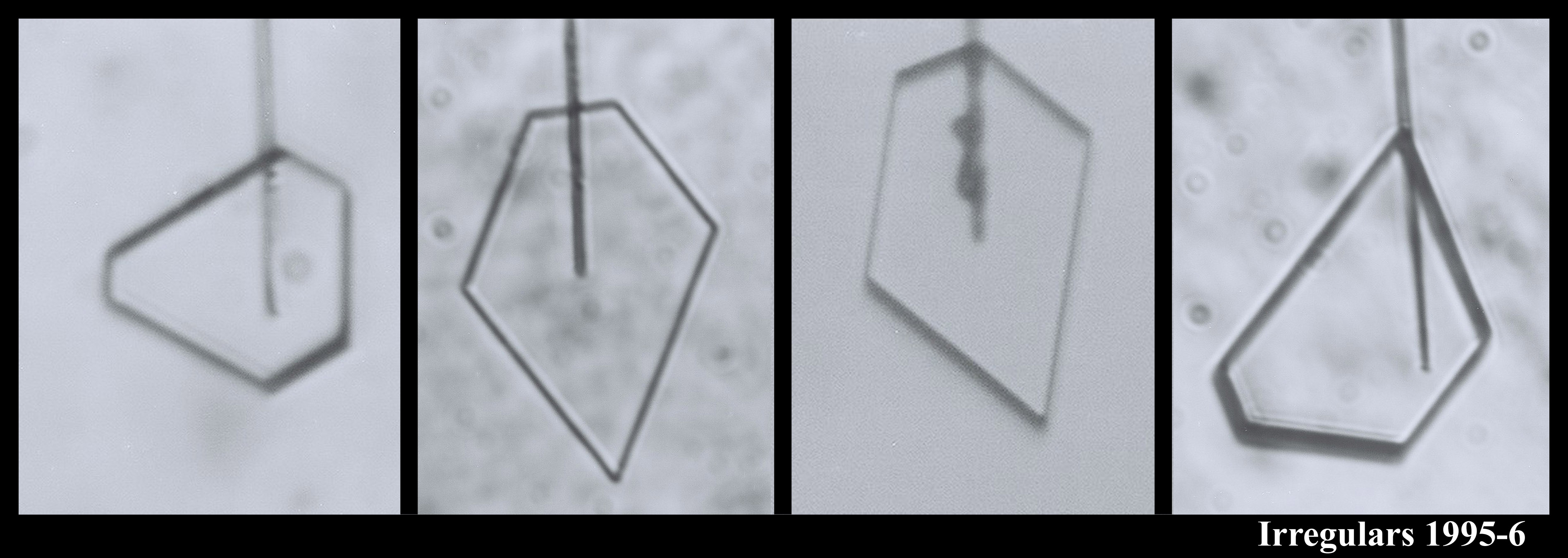
You can see that sometimes a crystal is 5-sided. But the angles between the prismatic faces are always multiples of 60 degrees. I don't think I'll ever see a 5-sided snow crystal that looks exactly like a pentagon.
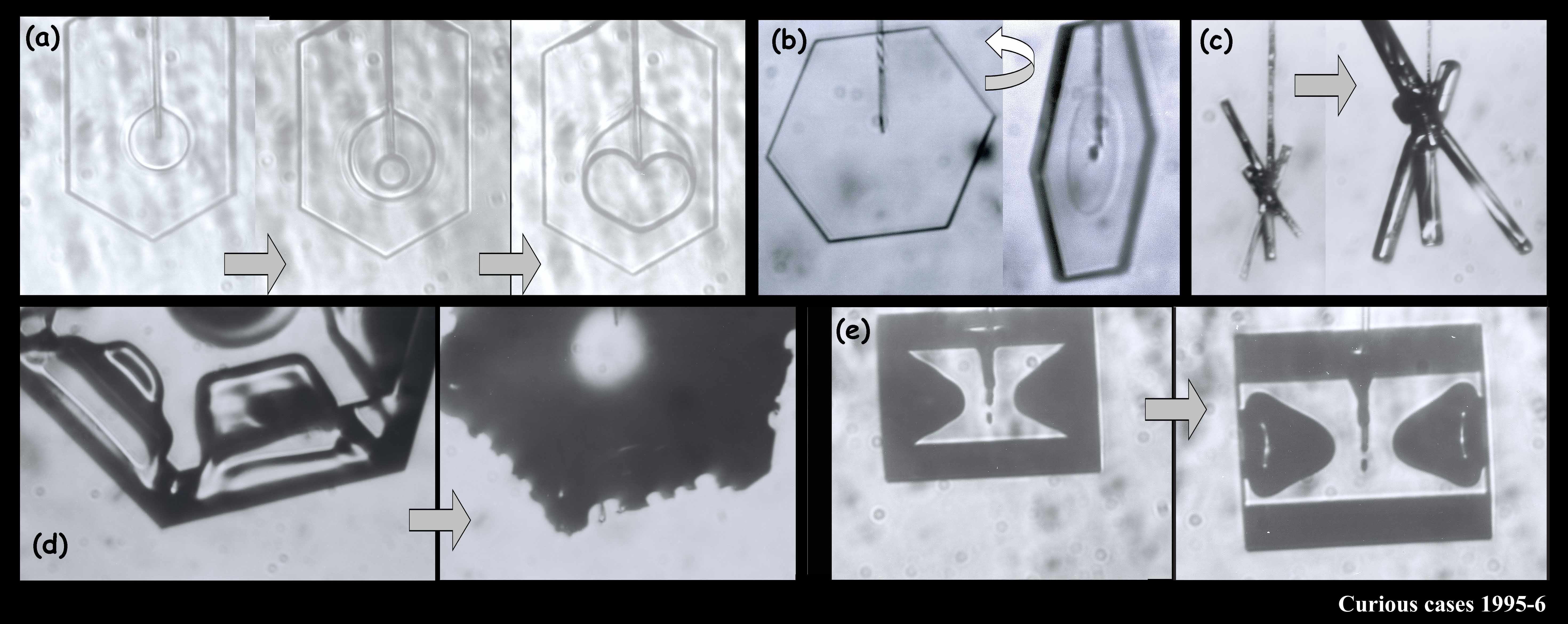
The large crystal at the bottom left & middle was starting to melt. The melting formed cusps on the edges of the face. The one at the top right is called a bullet rosette. These crystals are very common in cirrus clouds and other very low-temperature clouds. The sequence at the upper left shows something we can do with a capillary: we can suck the crystal out from the inside. In that case, I put a vacuum on the other end of the capillary and a void started to form. Then, inexplicably, a crystal started growing inside the void! You never know what will happen in these experiments.
By this time next year, I hope to be able to show new crystals we grew. And sometime soon after that, have some reliable results.
-- Jon
Caution!
February 1st, 2012Hoar. It's just a white coating on things, so why does it make everything look more interesting?
I saw this hoar coating on a plastic trash-can lid:
The hoar frost on the lid had various whirls, just like I've seen on the plastic surfaces of car door handles and side-view mirrors. This hoar was a little different though in that the crystals were definitely sticking up and not laying flat on the surface. Nevertheless, the fact that they show a pattern at all, and are not just randomly oriented, means that there must have been a liquid film of water that first froze to the surface. The film froze, producing a pattern of crystal orientations on the surface, and these orientations were not revealed until the hoar frost grew. Hurray for hoar!
Here's another warning:
The hoar crystals are longer on the raised lettering, particularly near edges. This is not because such places are further from the ground, but because they have more radiative cooling (due to their more expansive view of the sky) and can stick out into regions with a greater density of water vapor molecules.
If you click on the images, you can see the crystals a little better. But I forgot my tripod on this particular morning (I took the shots after I got to the office), and so the images aren't as crisp as my other close-up shots.
- Jon
Snow on a Freshly Frozen Pond
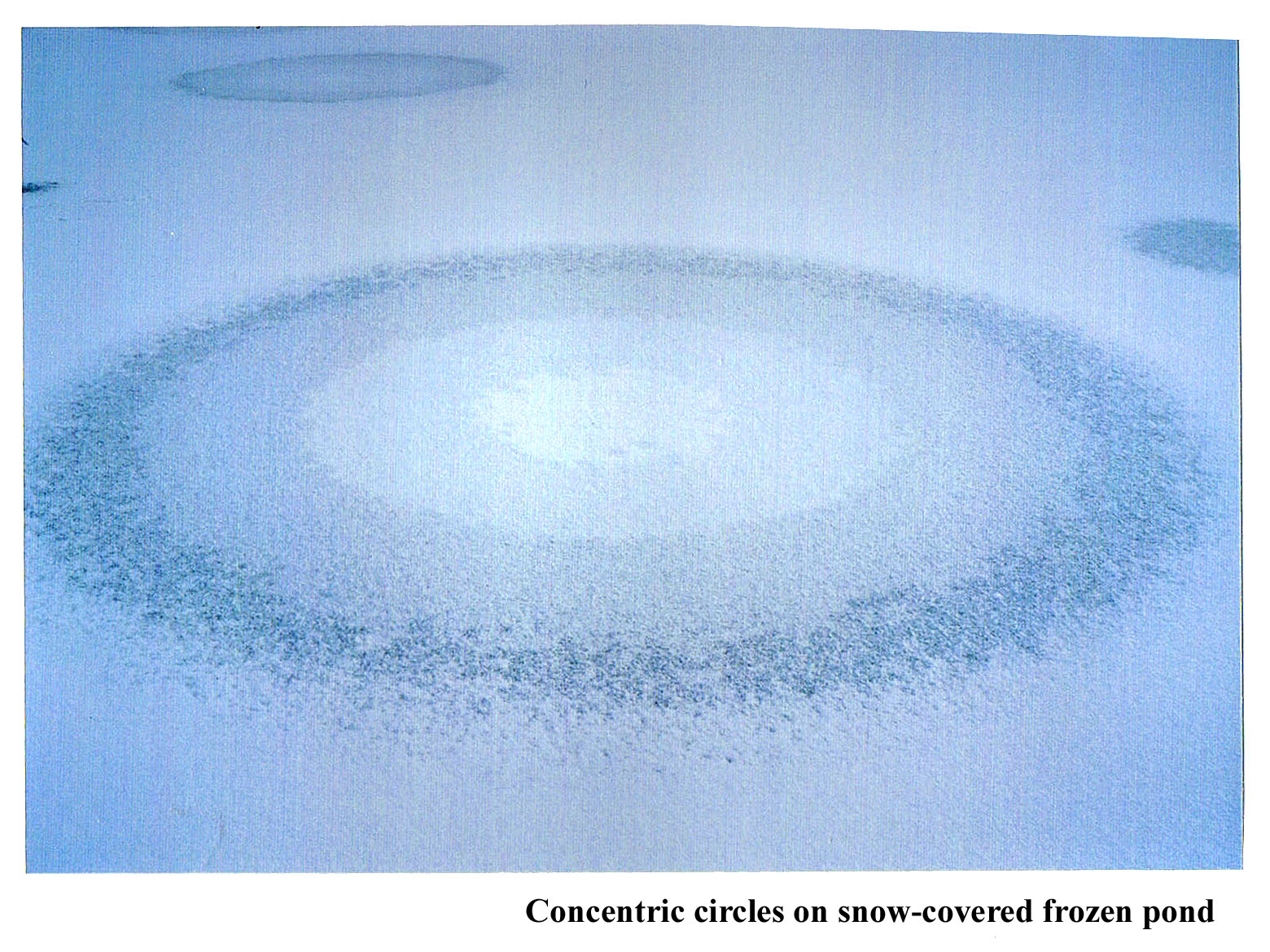
January 15th, 2012Back when I was doing post-doctoral work in Boulder, Colorado, Charlie Knight, the head of my lab, introduced me to strange ice phenomena. The most memorable one happened after the weather had been sub-zero for a few days and then we got some snow. When this happened, we stopped work and drove out to some shallow ponds to look at the patterns on the surface. Sometimes odd, concentric circles formed.
To see the size of the rings, check out the overview.
The guy in the background is Charlie. He is sawing through the ice to get a sample. Behind him are two visitors who came out with us that day. The ice was about 2" thick, if I remember right, and would make some cracking noises sometimes as we walked on it.
I don't know if he figured out the cause of the pattern. I never made any progress in understanding it. Anyway, what seems to happen is that water gets pushed out through a small hole in the ice, and the water apparently spreads out in a circular region. But why does the lightness of the ice change in nearly equally spaced, discrete steps? And why is it whitest in the center?
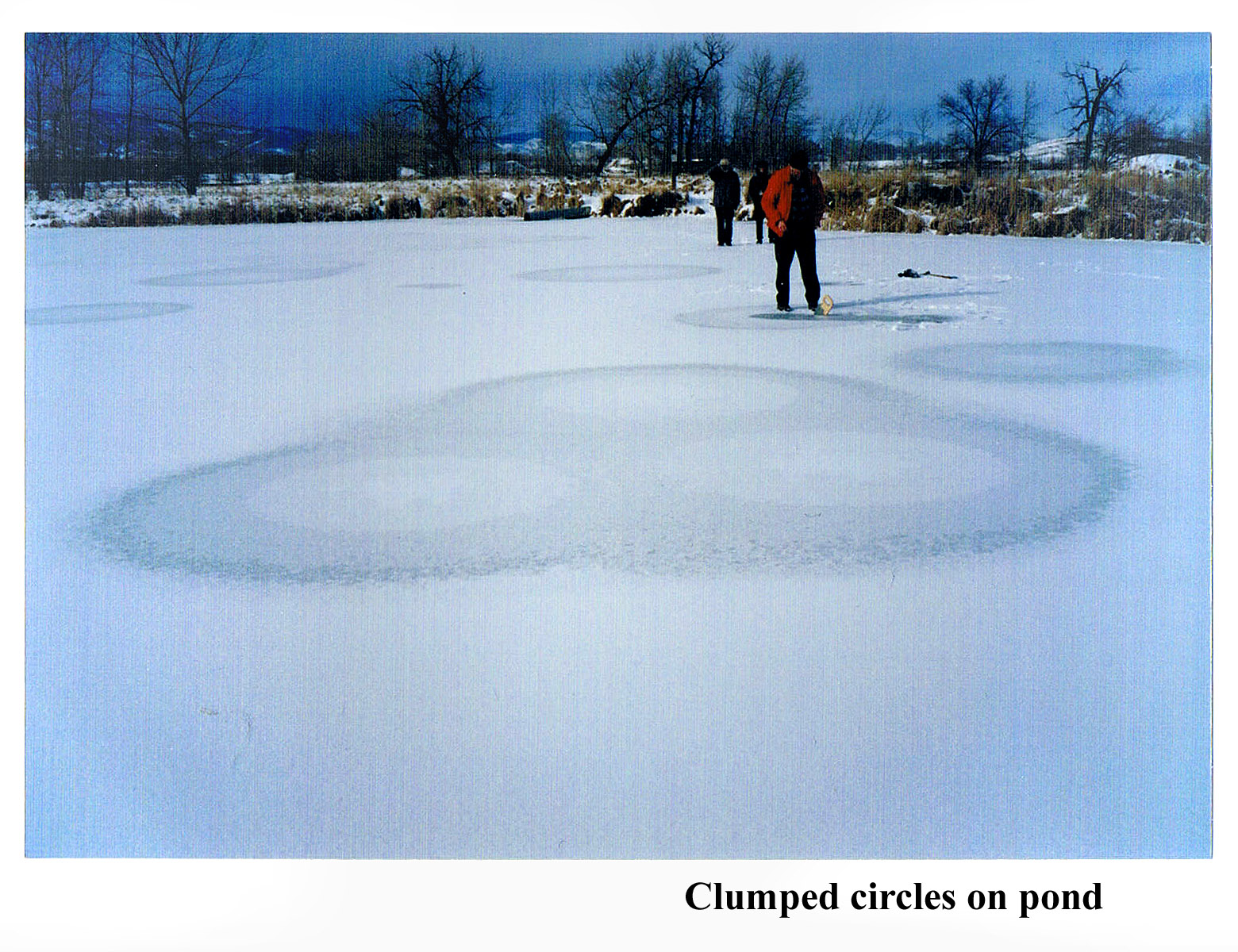
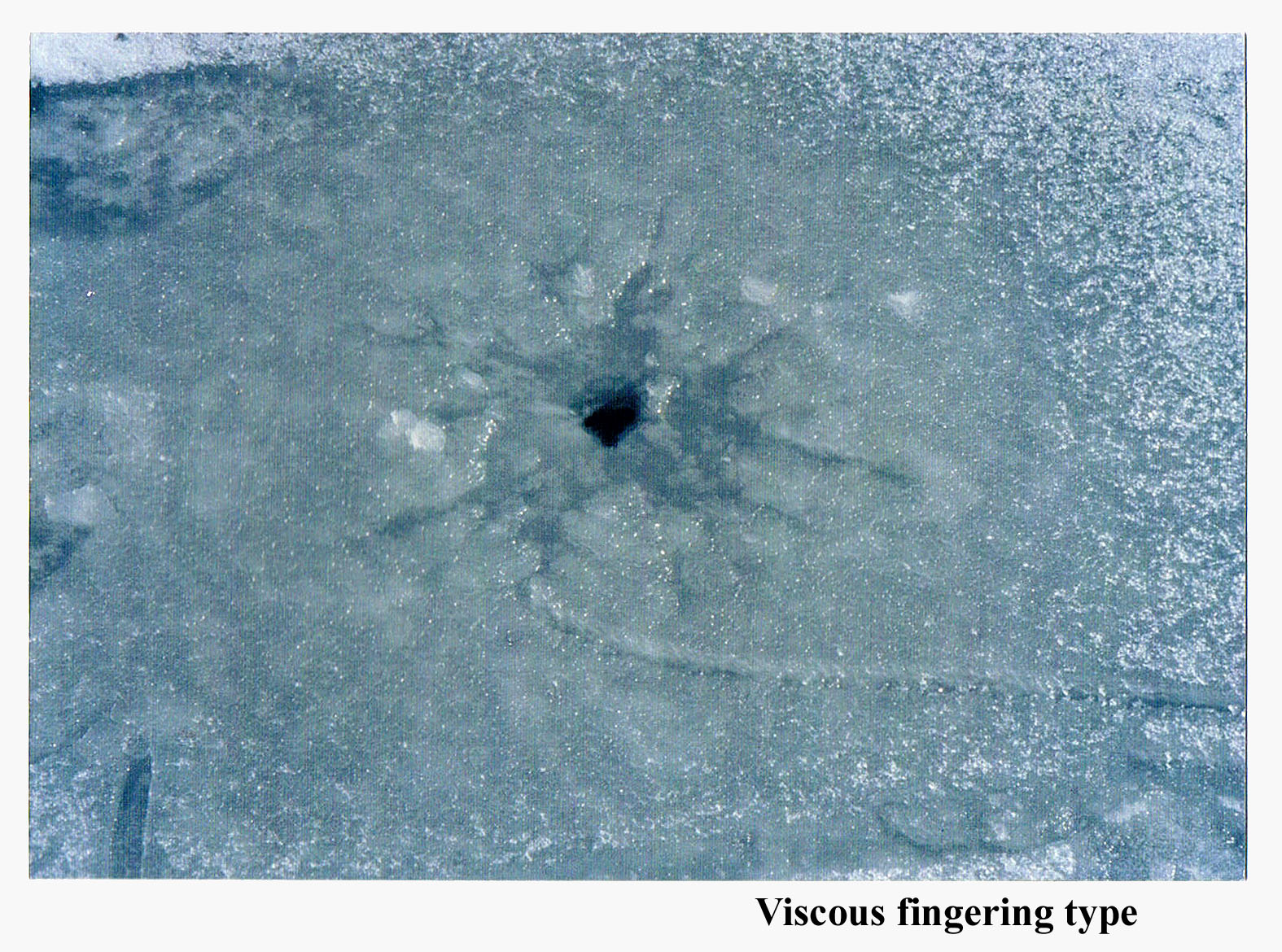
I figured that if water flooded over the ice in discrete steps (day-night temperature fluctuations, as we think happens with the pancake ice?), then the region in the center would be the darkest, not the whitest. For example look at this counterexample.
This shows the hole where water comes out, but the water floods outward in a ragged fashion, not like a concentric circle. This type of flow has been studied a lot in the laboratory and has the technical name "viscous fingering". Anyway, notice that the region near the center is darker, not whiter.
Any ideas about the concentric circles?
--Jon
The Six-fold Nature of Snow
March 15th, 2011How the crystal got its “six”
Ice Forms on Slow-moving Water I: Caterpillars and Cellular Dendrites
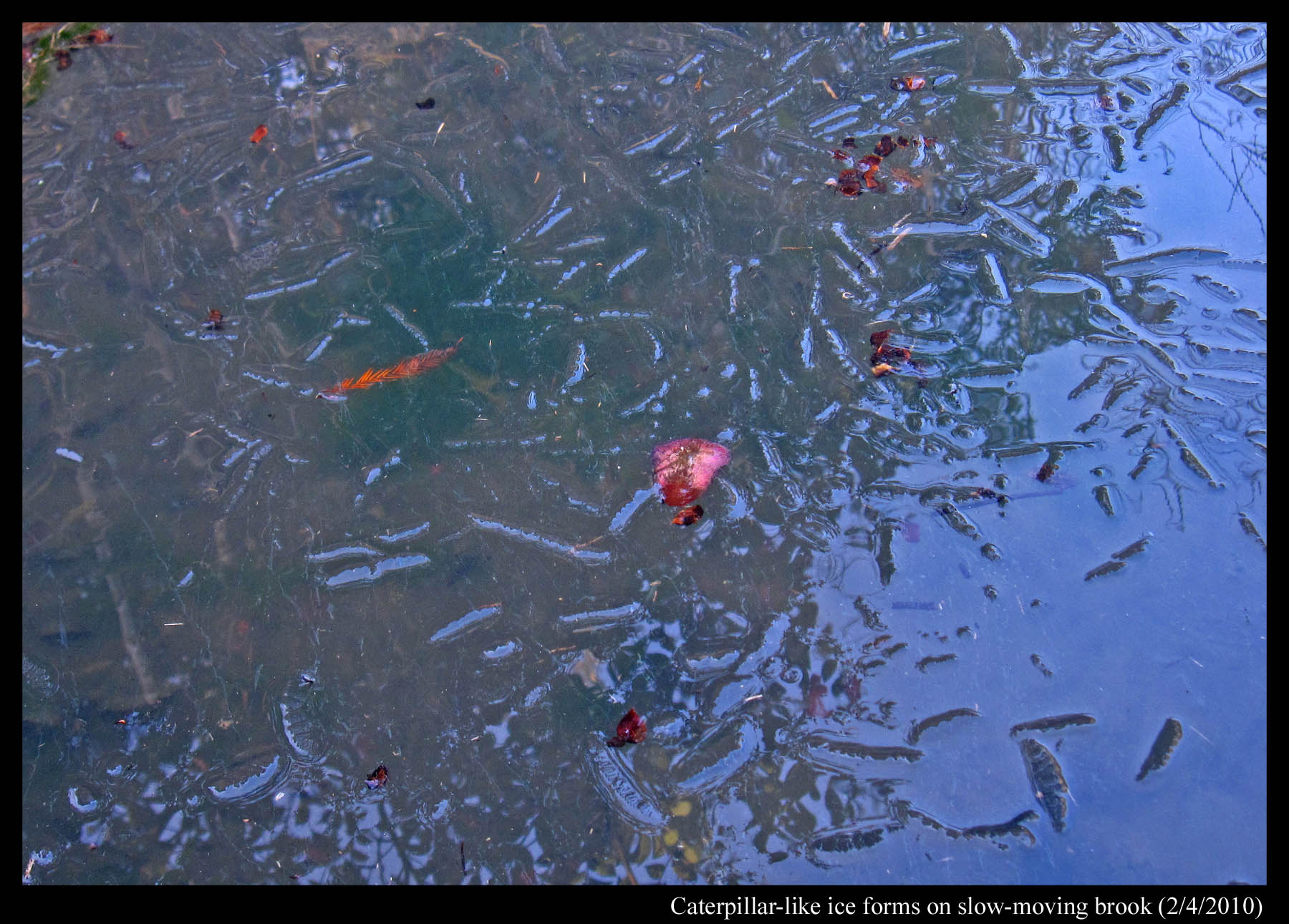
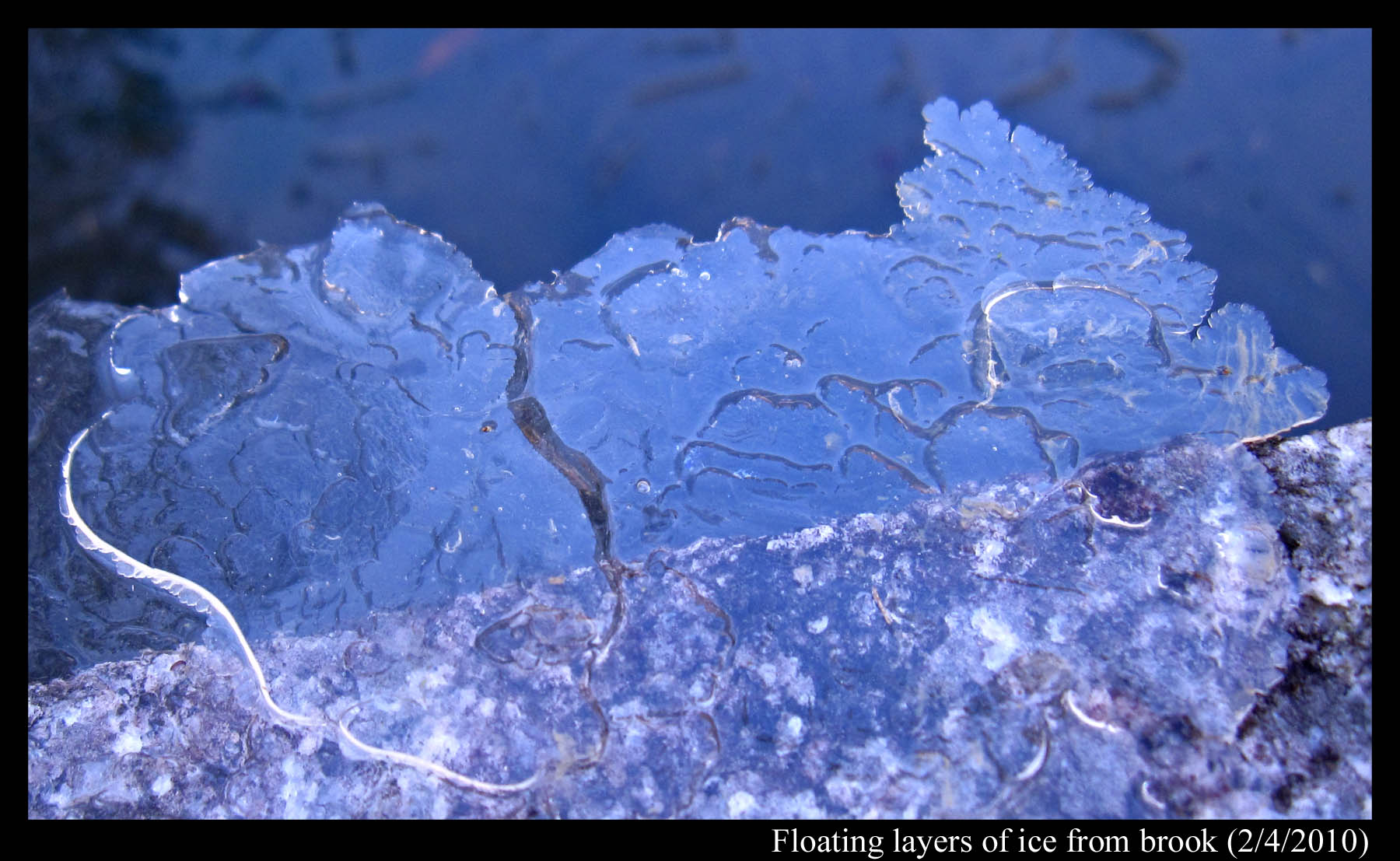
January 15th, 2011During my last winter in Japan (2009-2010), I would walk around a neighborhood park on frosty mornings, looking for interesting ice forms. It was in this park that I found one rock (only one!) that on some mornings would sprout hair-like ice, arising from liquid water within (see the last images in my “Ice on the Rocks” post, Jan 27). This park also has a small, slow-flowing brook that, despite the relatively warm conditions, often freezes over. Usually, upon freezing, it shows an ice pattern consisting of many long (~ one foot) straight lines – a typical pattern you usually see on glaciated puddles and ponds. But on the morning of February 4, at one spot right before the water tumbled over a waterfall, the ice surface looked slightly different. It had lines, but the lines were short, thick, and bumpy (see photo below), looking a bit like black-blue caterpillars scattered about.
From the small bridge spanning the brook, I reached down, pulled some ice out, and was shocked at what I saw. This was not “solid” ice, but rather a bunch of very thin ice plates loosely resting on each other – somewhat like a deck of cards spread out in a fan, though in this case, each ice plate had its own size and shape. Also, unlike other thin ice plates I’d seen before, these ones resembled neither the fast-growing ice dendrites (the snow-crystal-like, branched forms) nor the slow-growing ice discs. The photo below also shows that the plates were big – the section shown being several inches across.
Over larger streams and faster-moving water, ice can develop into something called frazil ice. I’ve no experience with frazil ice, never having lived in a cold-enough region, but I this caterpillar ice may be different. For one, the water was extremely slow-flowing. I could not discern the flow, even in ice-free regions, whereas the descriptions I’ve read about frazil ice involve easily discernable flow rates, flow rates that introduce turbulence, crystal collisions, and mixing below the surface. Also, the ice crystals I saw were much larger than the millimeter-sized pieces I see reported for frazil ice. So, the caterpillar form might be a transitional form, between frazil and that over stagnant water.
Hoared Hail and Coraline Cups
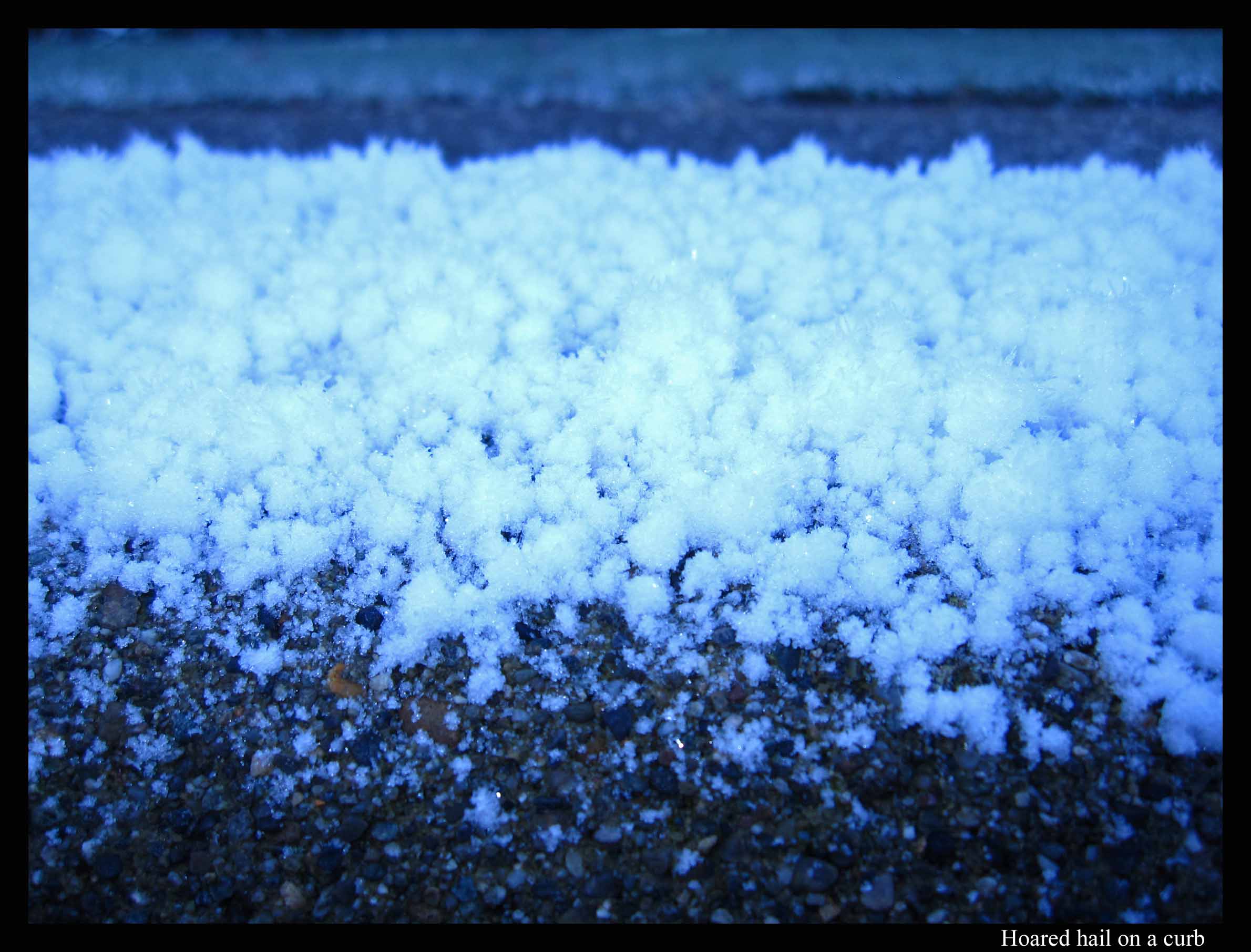
December 31st, 2010As far as I could tell, nobody had predicted hail last night, yet there it was on the ground, the largest hail I’ve ever seen here in the northwest. It fell on wet ground, freezing to the surface and then growing hoar columns, making the ground white and crunchy.
The parking lot in front of our apartment was covered in ice, mostly clear (i.e., "black") ice, yet, because of the ice lumps, it was not slippery under my boots. I kept expecting to slip, but never did. On the curb, where it was a little colder, the hoar was much thicker, looking like an inch of snow.
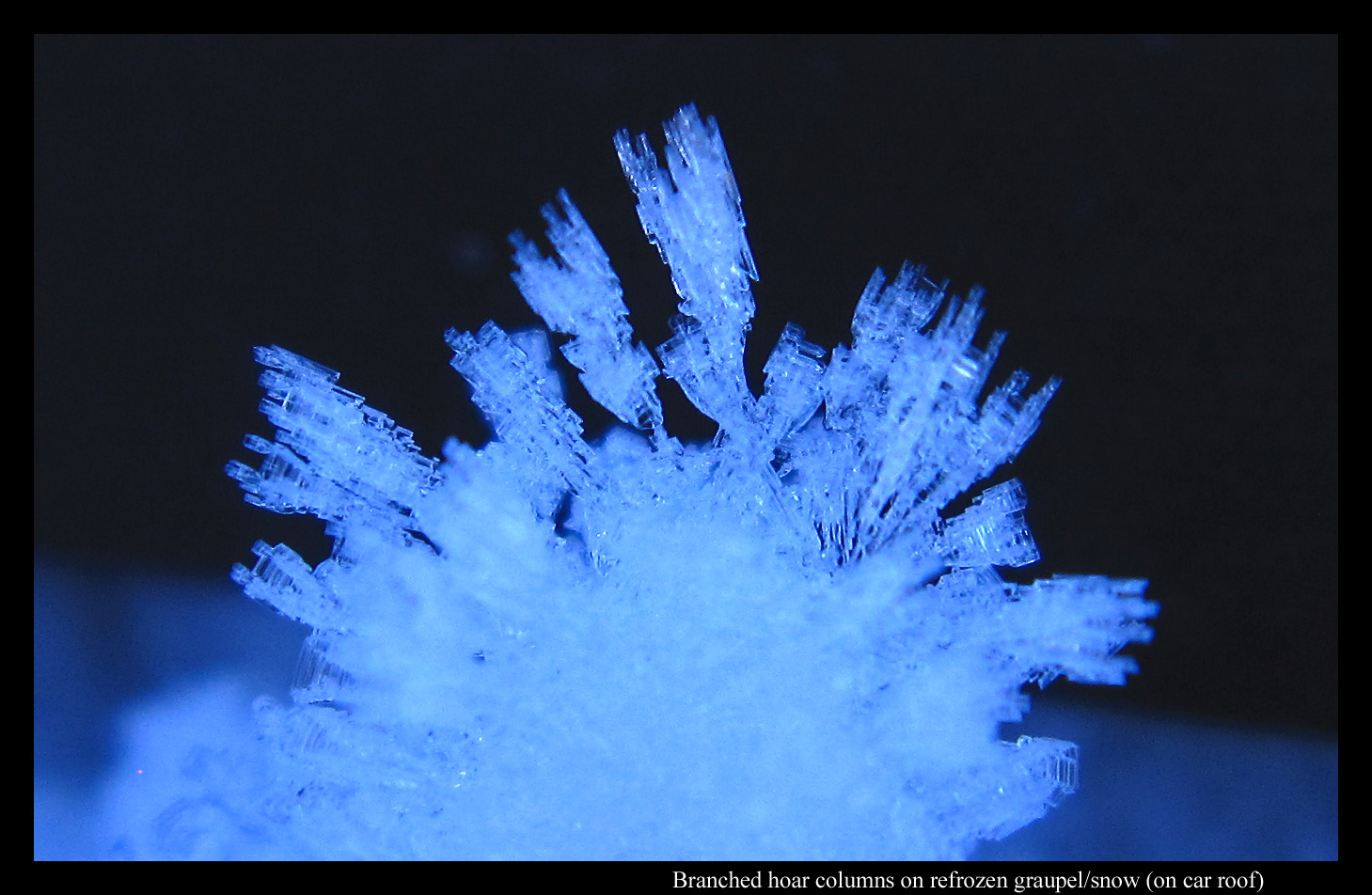
Same story for the tops of cars, where it had been coldest. The temperature was such that the hoar was mainly columnar. Columnar hoar, indeed all hoar, grows just like snow – when an excess of water molecules deposit from the vapor – and yet columnar hoar tends to develop more in the “cup” (C1b) and “scroll” (C1i) forms (see my Feb. 14 posting for the meaning of the symbols).
But unlike the pencil-like columnar forms of falling snow, these cups and scrolls grow broader at their growing end, even branching out into a pattern a bit like coral.
And if you look closely at the above shot, you will see that the “branches” grow along the same axis as the crystal from which they sprout. (For the above shot, I put a piece of black cloth in back to show the boundaries more clearly.) Such branching contrasts with that for tabular crystals, such as the ones on the familiar six-branched snow crystal.
Why do the columns widen at their growing ends, thus making a cup-shape, why do the cup rims sometimes curl into scrolls, and why do they branch out? I suspect the reason for all three (though not a complete reason) is that the humidity next to the growing crystals is very high – higher than that surrounding the typical column form that drops from the sky. Unlike the latter case, where the humidity is too low for the prismatic faces to grow outward, at least at any rate near that of the basal, here both the basal and prismatic faces grow at comparable rates. Such growth behavior also depends on the temperature, for reasons that still elude us.
- JN
More Tales of Mystery and Observation
December 1st, 2010When I stepped out early Saturday morning, the air seemed relatively warm, particularly compared to the cold snap we had last week. Indeed, it was much warmer, and yet the parking lot in our apartment complex had a glaze that was much more dangerous than that during the cold snap.
But it was the frost that I noticed. Of course, the air was relatively warm, but the clear sky cooled the surface. Recently, snow melted, leaving plenty of open water to evaporate – perfect conditions for film frost and hoar.
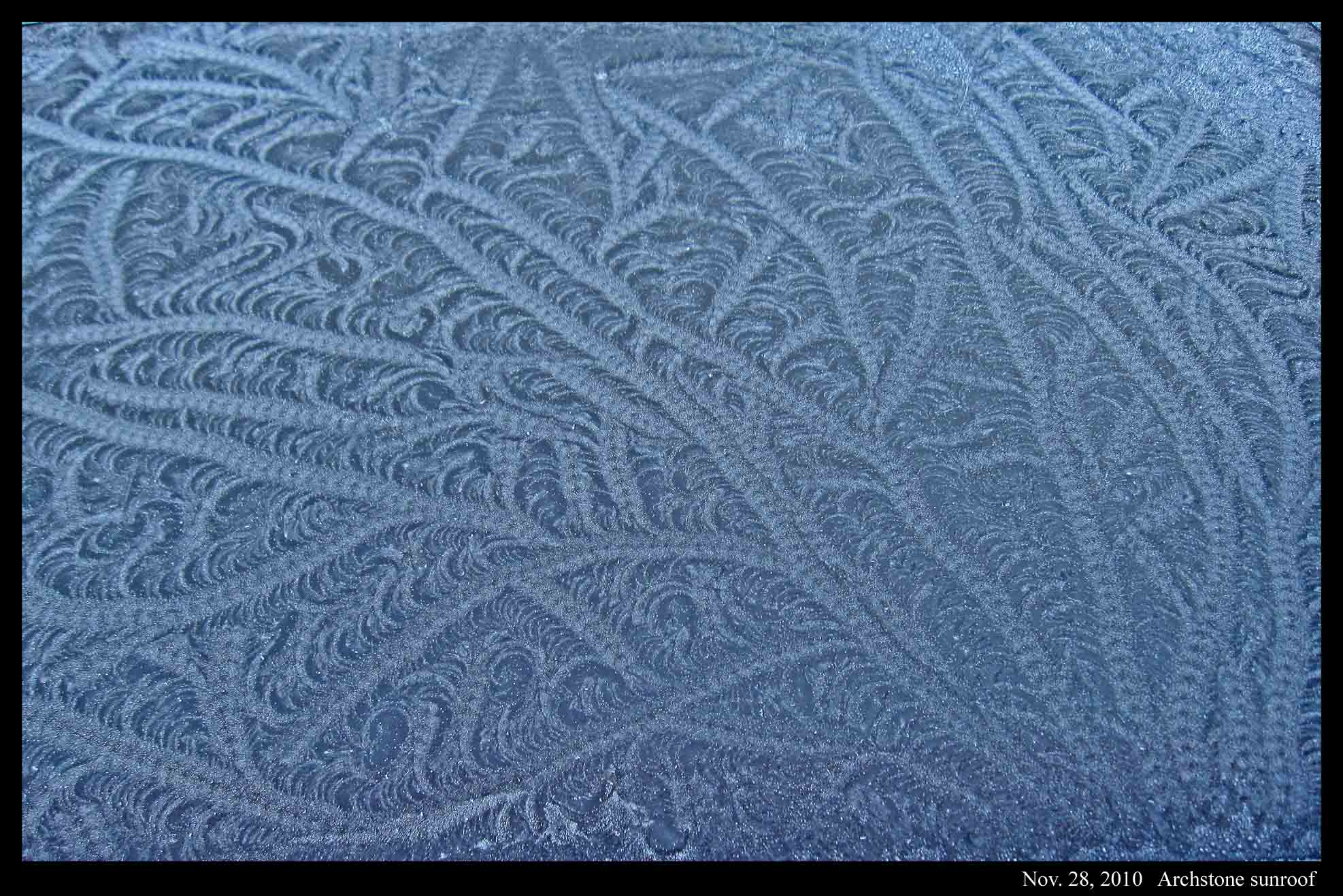
I saw “striped-tail” film frost(1) on two car roofs, both times on the sunroof glass. Why only on the glass? Perhaps the glass, being a poorer conductor of heat, had a lower surface temperature. This lower temperature would have produced a thicker film of water, and the thickness of the film seems to influence the pattern. The bigger mystery though is the cause of the pattern. In a short online article(2) last year, I suggested a cause for the stripes on each tail, though I can offer no explanation for either the nearly uniform width of the tails or the meandering. In the case below, the pattern is dense with lazily wandering striped tails. When I look at it, I think of seaweed. The metal car surfaces often had nice curving film-frost with dense hoar, while others had or condensed droplets with more isolated, spiky hoar. The latter appeared on my own car.
The Window of Many Cacti
February 14th, 2010The resemblance may be a bit more obvious in the following shot, which I took two years ago on seeing this form for the first time.
How to classify snow crystals
February 14th, 2010According to Edward LaChapelle’s Field Guide to Snow Crystals (1969), the most widely used classification for falling ice is a system of 10 types from the International Commission on Snow and Ice, which came out in 1951. A few years later, ice researcher Ukichiro Nakaya published a new system with four times the number of ice types. The number doubled 12 years later in 1966 when Magono and Lee published an extension of Nakaya’s system. Of all systems, I think Magono and Lee’s classification of 80 types gets the most use nowadays, so I show it here to help make more people aware of it.
To classify a crystal, you simply look at the table below and find the example that most nearly resembles your crystal. This table is a scanned copy of the one in LaChapelle’s book, with some markings cleaned up and a little color added. Click on it to enlarge.
For example, the crystal in Mark's Feb. 14 posting is P1c, a broad-branch crystal.
The number 80 seems large, but even this system has notable omissions. Magono and Lee include graupel (R4a, R4b), which are crystals that collided with many supercooled droplets, but they exclude crystals that collided with and adhered to other crystals. That is, they exclude snowflakes. Other omissions include distinct forms like the spearhead and seagull types as well as sub-divisions of forms they do include; for example, plates like P1a except with unequal sides such as the oft-sited trigonal forms (alternating prism faces are shorter/longer), and hollow columns like C1f except with hollows on all faces. And although they include 12-branched crystals, they don’t include 18 and 24-branched forms. They probably had a good reason for excluding these forms, but it would be nice to have a more complete table for the avid naturalist to refer to.
Choji Magono was a professor of geophysics at Hokkaido University in Sapporo Japan, and C. W. Lee was his student. I’ve known about other work by Magono for some time, but I’ve never found any other publications by Lee. I recently asked about Lee to someone who once was a student there, and he told me that Lee returned to North Korea soon after getting the PhD, apparently never to be heard from again. It sounds like a sad ending for a once very promising young researcher. If you can read this Lee, here’s a big thanks for your great dissertation work.
- JN